摘要
Sodium-glucose cotransporter2 (SGLT2) inhibitor 為最新型口服降血糖藥,被核准於治療第二型糖尿病之二線用藥。最近的文獻證據指出使用 SGLT2 inhibitor 可能會增加糖尿病酮酸中毒 (diabetic ketoacidosis,DKA) 之風險,其特徵為酮酸中毒發生時血糖值可能為輕至中度上升,故又稱為 euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis (euDKA)。本案例報導一名患有第二型糖尿病之64歲女性,Hb-A1C 14.5%,使用 dapagliflozin 七天後,因意識不清伴隨跌倒由家人送至急診就醫。檢驗值呈現血糖值略高 (181 mg/dL)、酸中毒 (pH 6.9、HCO3- 6.3 mmol/L)、及酮血症 (5.4 mmol/L)。此病人被診斷為 euDKA 並轉送至加護病房持續照護,治療四天後,酮症酸中毒情況緩解。euDKA 在沒有顯著的高血糖情況下,可能會延遲病人本身和醫療照護者辨識糖尿病酮症酸中毒出現的急迫性。藉由此案例的呈現,希望可以加強醫療照護人員對於 SGLT2 inhibitors 可能造成罕見但危及生命之副作用的認識。
關鍵字: Sodium-glucose cotransporter2 (SGLT2) inhibitor、diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)、euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis (euDKA)
壹、前言
Sodium-glucose cotransporter2 (SGLT2) inhibitor 以全新的機轉來促進血糖值之控制,其作用與胰島素之分泌及組織利用無關,藉由抑制葡萄糖在腎臟的再吸收而促使葡萄糖由尿液中排除,借此達到降血糖的作用。然而美國 FDA 在2015年發布警訊指出 SGLT2 inhibitor 可能在體內產生過多的酸,增加糖尿病病人產生糖尿病酮酸中毒 (diabetic ketoacidosis,DKA) 的風險1。有鑒於 SGLT2 inhibitor 為新機轉藥物且在第二型糖尿病血糖控制的角色日趨重要,醫療照護人員應評估其安全性及找出並降低可能導致 DKA 的危險因子2,以確保病人用藥安全及避免發生藥物不良反應。
貳、案例報告
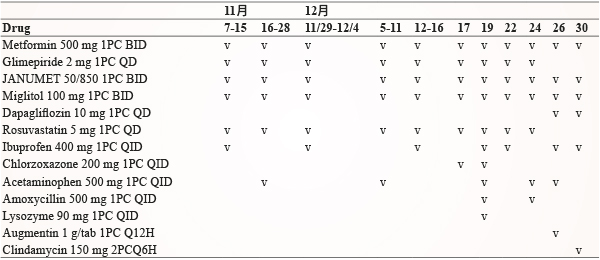
一位64歲女性,身高166公分,體重52公斤,BMI:18.8 kg/m2,患有第二型糖尿病病史,規律使用口服降血糖藥控制血糖,包括 metformin 500 mg BID、miglitol 100 mg BID、glimepiride 2 mg QD 及 janumet 50/850 BID。最近因牙痛到牙科診所就醫,接受根管治療與傷口引流,因為傷口範圍過大且癒合情形不良,病人接受醫師建議於105年12月22日至本院牙科做後續的處置。
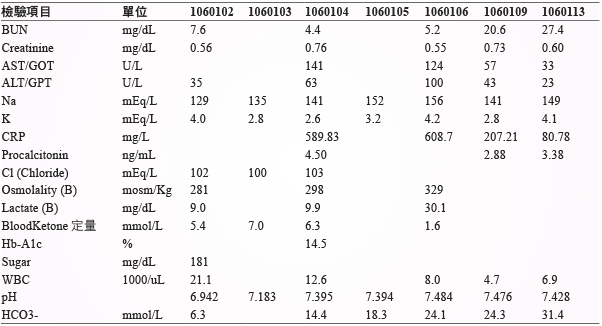
由於血糖控制成效不佳,內科診所醫師建議開始施打胰島素,但病人拒絕,醫師於12月26日將 glimepiride 取代成 dapagliflozin 10 mg QD,使用7日後,因意識不清伴隨跌倒,由家屬於1月2日晚間送至本院急診就醫,在急診時生化檢驗發現病人有嚴重的代謝性酸中毒,血中酮體高達5.4 mmol/L (正常值應小於0.6 mmol/L),pH 值6.9,血糖值181 mg/dL,anion gap 21,osmolality gap 11,家屬反映病人最近因牙痛而使用止痛藥及塗抹綠油精,醫師安排毒物篩檢以排除藥物中毒的情形,詳細生化檢驗值 (表一、表二)。於急診診治時,即開始給予 sodium bicarbonate 校正酸中毒的情形並停用 dapagliflozin。
表一 住院期間檢驗數值
表二 藥物分析
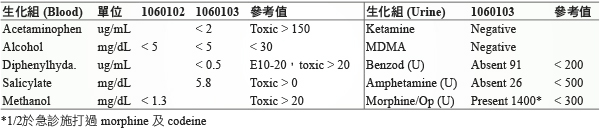
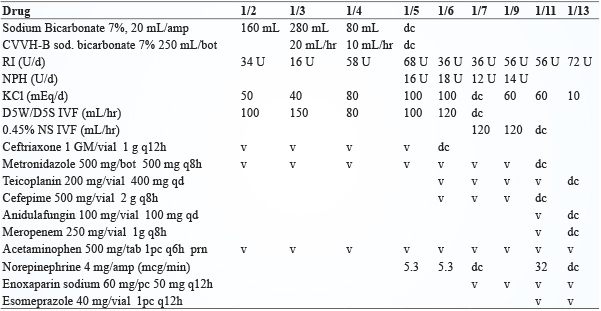
1月3日血中酮體仍偏高 (blood ketone 7.0 mmol/L) 且酸中毒改善情況不佳 (pH 值7.1),腎臟科醫師於1月4日上午安排血液透析,在透析過程中因病人血壓不穩定而在透析結束後轉送至加護病房做後續的照護,重症醫師持續給予輸液及鉀離子補充、投予 insulin 並視情況以 sodium bicarbonate 校正酸中毒,檢測 A1C 為14.5%,1月5日 DKA 情況改善,停用 sodium bicarbonate。評估病人口腔上顎傷口感染情形,WBC 12,600/uL,CRP 589.83 mg/L,procalcitonin 4.50 ng/mL,經診斷為蜂窩性組織炎合併膿瘍形成,並給予 ceftriaxone、metronidazole 抗生素治療,1月6日因低血氧執行氣管內插管並使用呼吸器,1月7日出現左下肢深層靜脈栓塞,投予 enoxaparin 治療,此病人於1月19日成功脫離呼吸器,後續照護包括血糖控制、抗生素及深層靜脈栓塞治療。住院前用藥及住院中用藥 (表三、表四)。
表三 近2個月住院前用藥 (資料來源:雲端藥歷)
表四 住院中用藥紀錄
參、討論
一、SGLT2 inhibitor
1835年法國科學家從蘋果樹樹皮分離出 phlorizin,在動物實驗中發現可以增加尿糖的排出使得血糖降低,是最早的 SGLT2 inhibitor,在2013年3月美國 FDA 核准第一個 SGLT2 inhibitor,canagliflozin 上市,使得糖尿病治療用藥增加新選擇,後續 dapagliflozin 與 empagliflozin 也相繼上市,台灣於2014年10月核准 empagliflozin,隔年1月 dapagliflozin 亦在台灣上市。
血糖在腎臟的調控及利用是由腎髓質細胞消耗葡萄糖產生能量,而腎皮質細胞利用糖質新生產生葡萄糖來達到血糖在腎臟的進出淨平衡為零,藉由胰島素的抑制與腎上腺素的刺激來調控腎臟的糖質新生。正常人每天經由腎絲球過濾出約180 g 葡萄糖到腎小管,而這些葡萄糖幾乎由近端腎小管的 Sodium-glucose cotransporter (SGLT) 再吸收回到血液中,其中近90%由近端腎小管中的 SGLT2再吸收,剩餘的10%則由遠端的 SGLT1吸收,所以正常人的尿液中不會有葡萄糖出現4。
正常人葡萄糖再吸收的上限約為200 mg/dL,當血糖大於200 mg/dL 時,多餘的葡萄糖會由尿液排除,但是糖尿病人葡萄糖再吸收的閾值大於200 mg/dL,造成血中葡萄糖濃度增加,使得體內呈現高血糖的現象,SGLT2 inhibitor 藉由抑制腎小管的 SGLT2來降低再吸收的閾值及增加尿糖的排除達到降血糖的效果。
二、Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis
美國 FDA 在2015年發布了一則關於糖尿病治療新藥 SGLT2 inhibitors 的藥物安全警訊,警告 SGLT2 inhibitors 可能導致酮酸中毒 (ketoacidosis)。美國的藥物不良反應通報系統 (FDA Adverse Event Reporting System, FAERS) 資料庫中,已經有多起酸中毒的通報案例,包括:糖尿病引起的酮酸中毒 (diabetic ketoacidosis)、酮酸中毒 (ketoacidosis)、酮症 (ketosis)。在臨床試驗中,CANVAS study 在17,596名受試者中有15名產生 DKA,其中12名使用 canagliflozin,其發生率小於0.1%,除此之外,DECLARE study 與 EMPA-REG study 也都得到類似的結果,其產生 DKA 的比率也都小於0.1%。利用 PubMed 搜尋2013年到2016年相關個案報告與本案例比較整理如 (表五)。
表五 案例比較
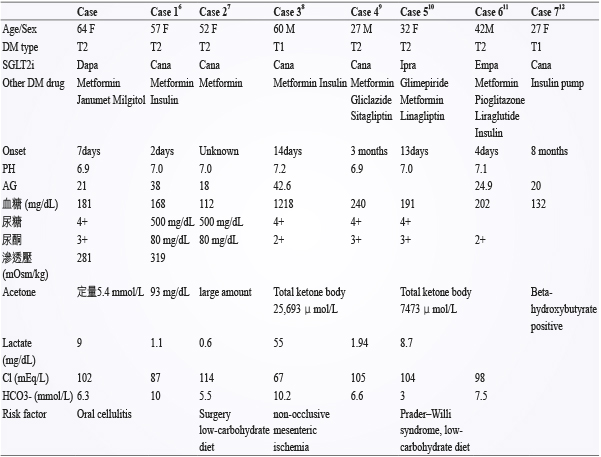
這類 SGLT2 inhibitors 導致的酮酸中毒和典型的糖尿病引起的酮酸中毒 (diabetic ketoacidosis, DKA) 不同,DKA 較常發生在第一型糖尿病的病人,當血中的胰島素過低或長期空腹時,一般會伴隨高血糖的狀態 (> 250 mg/dL),但 SGLT2 inhibitors 導致的酮酸中毒的這些病人多為第二型糖尿病,其血糖可能為正常、略高或過高 (> 250 mg/dL),當血糖值 < 200 mg/dL 產生之 DKA,被稱為 euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis (euDKA)。而 SGLT2 inhibitors 造成血中酮體上升的可能機轉如下3,5:(1) SGLT2 inhibitor 會直接刺激 α-cell 分泌 glucagon,而 glucagon 則會促進肝臟的 ketogenesis。(2) SGLT2 inhibitor 可能會增加 ketone body 的再吸收。在動物研究發現使用 phlorizin 會增加 acetoacetate 在腎小管的再吸收,SGLT2 inhibitor 可能也會藉由類似的機轉增加 ketone body 的再吸收。(3) Insulin 劑量減少。SGLT2 inhibitor 合併使用 insulin,因為血糖降低所以減少 insulin 劑量以避免低血糖,insulin 減少則會增加脂肪組織的 lipolysis 及肝臟的 ketogenesis,結果造成 ketone body 增加。(4) SGLT2 inhibitor 可能透過增加 glucagon 進而抑制 insulin 分泌。
SGLT2 inhibitor 造成的 euDKA 通常有下列特性:(1) 輕微上升的血糖 (< 200 mg/dL),(2) 陰離子間隙高 (high anion gap),(3) 血中酮體升高或尿酮升高。而容易引起 euDKA 的誘發因子為13:胰島素劑量過低、空腹時間過長或使用低卡路里飲食、急性的疾病狀態、感染、創傷等,而酒精濫用、低血容積、急性腎損傷等都可能會加重 euDKA 的嚴重度。
如果病人在服用此類藥物期間發生酮酸中毒的症狀,包括:呼吸急促、呼吸困難、噁心嘔吐、厭食、腹痛、昏睡、意識改變、不尋常的疲勞困倦等,則須注意病人是否發生酸中毒,檢測病人尿液或血液中的酮體,評估後為酮酸中毒時,應立即停止使用 SGLT2 inhibitors,並治療酸中毒。
要降低 SGLT2 inhibitor 引起的 euDKA 則需避免誘發因子的產生:(1) 平常須保持適當的水分攝取,(2) 避免胰島素劑量調整波動太大,(3) 如果必需進行手術或從事高強度的活動,建議停用 SGLT2 inhibitor 至少24小時,(4)避免酒精、低卡路里或生酮飲食。
本案例在使用 dapagliflozin 第7天後,發現病人有意識不清的情形,血中酮體升高,呈現酸中毒的情形,按照 DKA 處理流程進行治療,依據文獻資料與回顧用藥時序,以 Naranjo score 評估表評分為6分 (表六),此案例經評估「極有可能」為使用 dapagliflozin 引起 euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis,已通報至全國藥物不良反應通報中心。
表六 藥物不良反應相關性之分析探討-Naranjo score 評估表

肆、結論
雖然 SGLT2 inhibitor 引起的 euDKA 發生率不高,但可能因血糖值在正常範圍而容易被忽略,當使用 SGLT2 inhibitor 的病人有 DKA 相關症狀出現時,建議檢測血液或尿液中的酮體,若是呈現酮酸中毒則應立即停用 SGLT2 inhibitor 並就醫接受治療。
Dapagliflozin Induced euDKA
Chia-Fang Lin, Hsuan-Ling Hsiao, Tzu-Cheng Tsai
Department of Pharmacy, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Linkou
Abstract
Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors are the newest class of oral antihyperglycemic medications to be approved for the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus as one of second-line therapy options. Recent evidence warns of an increased risk of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) with uncharacteristically mild to moderate glucose elevations (euglycemic DKA [euDKA]) associated with the use of SGLT2 inhibitors. A 64-year-old female patient with type 2 diabetes was brought to the emergency department with sudden onset of unconsciousness and fell down. She was started on dapagliflozin 7 days ago and before initiating dapagliflozin, her baseline Hb-A1C was 14.5%. Laboratory investigations revealed euglycemia (181 mg/dL), acidosis (arterial blood gas: pH 6.9, HCO3- 6.3 mmol/L) and ketonemia (ketone body: 5.4 mmol/L). She was admitted to the intensive care unit with a diagnosis of euglycemic DKA and recovered uneventfully four days later. The absence of significant hyperglycemia in this situation may delay recognition of the emergent nature of the problem by patients and healthcare providers. We present this case in hopes that it will enhance recognition of this potentially life-threatening complication.
參考資料:
1.U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Drug Safety Communication: FDA warns that SGLT2 inhibitors for diabetes may result in a serious condition of too much acid in the blood, 15 May 2015. Available from http://www.fda.gov/downloads/DrugSafety/UCM446954.pdf. Accessed February 15, 2017.
2. Goldenberg RM, Berard LD, Cheng AY, et al: SGLT2 Inhibitor–associated Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Clinical Review and Recommendations for Prevention and Diagnosis. Clinical Therapeutics 2016; 38: 2654-64.
3. Taylor SI, Blau JE, Rother KI: SGLT2 Inhibitors May Predispose to Ketoacidosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2015; 100(8): 2849-52.
4. DeFronzo RA, Norton L, Abdul-Ghani M: Renal, metabolic and cardiovascular considerations of SGLT2 inhibition. Nat Rev Nephrol 2017; 13(1): 11-26.
5. Ogawa W, Sakaguchi K: Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis induced by SGLT2 inhibitors: possible mechanism and contributing factors. J Diabetes Investig 2016; 7(2): 135-8.
6. Andrews TJ, Cox RD, Parker C, et al: Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis with Elevated Acetone in a Patient Taking a Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitor. J Emerg Med 2017; 52(2): 223-6.
7. Bonanni FB, Fei P, Fitzpatrick LL: Normoglycemic ketoacidosis in a postoperative gastric bypass patient taking canagliflozin. Surg Obes Relat Dis 2016; 12(1): e11-2.
8. Gocho N, Aoki E, Okada C, et al: Non-occlusive Mesenteric Ischemia with Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Lactic Acidosis Following the Administration of a Sodium Glucose Co-transporter 2 Inhibitor. Intern Med 2016; 55(13): 1755-60.
9. Adachi J, Inaba Y, Maki C: Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis with Persistent Diuresis Treated with Canagliflozin. Intern Med 2017; 56(2): 187-90.
10. Hayami T, Kato Y, Kamiya H, et al: Case of ketoacidosis by a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor in a diabetic patient with a low-carbohydrate diet. J Diabetes Investig 2015; 6(5): 587-90.
11. Rashid O, Farooq S, Kiran Z, et al: Euglycaemic diabetic ketoacidosis in a patient with type 2 diabetes started on empagliflozin. BMJ Case Rep 2016. Available from http://casereports.bmj.com.smhslibresources.health.wa.gov.au/ content /2016/ bcr-2016-215340.long Accessed February 15, 2017.
12. Bader N, Mirza L: Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis in a 27 year-old female patient with type-1-Diabetes treated with sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor Canagliflozin. Pak J Med Sci 2016; 32(3): 786-8.
13. Rosenstock J, Ferrannini E: Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis: A Predictable, Detectable, and Preventable Safety Concern With SGLT2 Inhibitors. Diabetes Care 2015; 38(9): 1638-42.
通訊作者:林佳芳/通訊地址:桃園市龜山區復興街5號
服務單位:林口長庚紀念醫院藥劑部藥師/聯絡電話:(O) 03-3281200 ext 2692

