摘要
第二型糖尿病 (T2DM) 及其相關併發症往往使得病人生活品質下降,也造成社會經濟的負擔。儘可能地控制血糖值接近非糖尿病範圍,被證實對於小血管併發症是有益處的,包括眼部、腎臟及神經的病變1。近年來,以腸泌素 (incretin) 為基礎理論的藥物如 dipeptidyl peptide-Ⅳ (DPP-4) inhibitors 及 glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists,前者降低 HbA1c 效果低於現行藥物,後者雖有不錯降低 HbA1c 的表現,但注射劑型為其不便之處;新一代機轉 sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT-2) 抑制劑,作用近端腎小管,藉由抑制腎絲球過濾的 glucose 被再吸收回體內,而促進尿液中血糖的排泄 (glycosuria),因此可用在第一型及第二型高血糖及肥胖病人,此類藥物口服吸收良好,有卓越降低體重效果且低血糖副作用極低,現已進入 phase 3 階段,可望為無法達良好血糖控制患者帶來福音。
關鍵字: T2DM、sodium-glucose co-transporter-2、incretin、GLP-1 receptor agonists、dipeptidyl peptide-Ⅳ inhibitors、diabetes
壹、前言
自從西元2000年至2010年間,糖尿病確診人數由一億兩千萬人增加至兩億八千萬人,其中有90%為 T2DM 病人2。糖尿病是一種因胰島素缺乏或拮抗胰島素功能的因子出現,導致血糖上升的疾病,美國糖尿病學會與歐洲糖尿病研究學會提出治療流程,治療目標希望能維持 glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) 值在6~7%間,而不發生低血糖副作用。理想的降血糖藥應兼備有效性、安全性及良好耐受性。現在的治療方式因受限於副作用 (尤其是低血糖及體重增加) 或使用禁忌,無法明顯減緩疾病的進程。
DPP-4 inhibitors (如 sitagliptin) 具備不增加體重及良好耐受性的優勢,約降低 HbA1c 0.6~0.9%,通常與其他藥物併用;GLP-1 類似物 (如exenatide、liraglutide) 雖然缺乏長期使用經驗,美國糖尿病協會 (ADA) 與歐洲糖尿病研究學會 (EASD) 已將此類列在治療建議中 (表一)1,其可降低體重,且在動物實驗證實可延長 β-cell 存活3,因此理論上可延緩疾病進程,但其注射劑型限制其使用方便性;最新一類的藥品 SGLT-2 inhibitor 於第三期臨床試驗顯示約可降低 HbA1c 0.7~0.8%4。本文將介紹新藥 SGLT-2 inhibitor 並對其臨床試驗的結果進行比較。
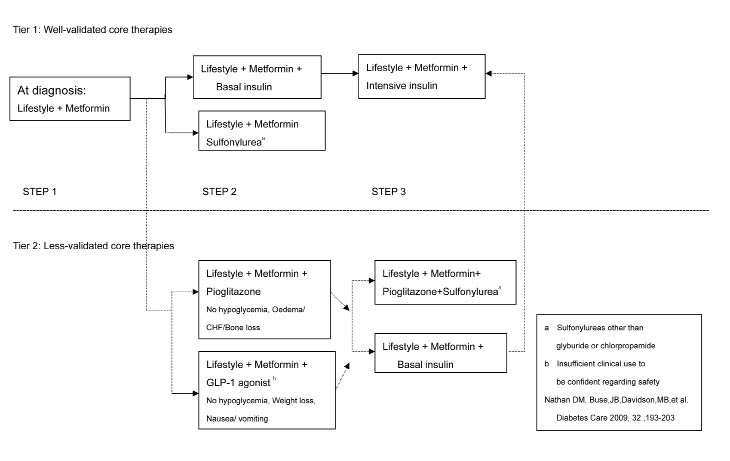
表一 ADA/EASD Consensus Treatment Algorithm1
貳、 Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT-2) 抑制劑
每天一個健康成人腎絲球約過濾180 g 的 glucose,其中只有大約1 %真正被排泄出體外,大多數 glucose 藉由 SGLT-2 作用在近端腎小管,被再吸收回體內。此類藥物具備高度選擇性競爭抑制 SGLT-2,因此抑制了腎臟對 glucose 的再吸收,而可促進尿液中血糖的排泄 (圖一),因此可用在第一型及第二型高血糖及肥胖病人。目前為止,不論動物或人體試驗皆未傳出低血糖反應5。目前此類藥物具備良好口服吸收率及專一性的有 sergliflozin 及 dapagliflozin,兩者皆為口服劑型且可降低體重4,6。常見副作用為鼻咽炎、下呼吸道感染及頭痛。
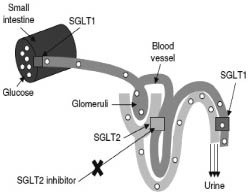
圖一 SGLT-2生理機轉7
一、Sergliflozin
目前臨床試驗進行到 phase Ⅱ,結果顯示服用 sergliflozin 500 mg 及 1000 mg 都有良好耐受性,且尿液中排出 glucose 的量隨著劑量調高而增加;18位肥胖受試者以 Sergliflozin 治療的第15天,與安慰組相比體重減輕了1.5 kg,即使以高劑量使用在正常人身上仍不會造成低血糖。副作用為輕微頭痛、眩暈及噁心8。
二、Dapagliflozin
在 Komoroski et al. phase Ⅲ,收納546位服用 metformin (≥ 1500 mg) 但仍無法良好控制血糖的病人,隨機分派成四組,除了皆服用穩定劑量的 metformin 外,分別給予一天一次2.5 mg、5 mg、10 mg dapagliflozin 及安慰劑,進行24周雙盲試驗,結果顯示服用 dapagliflozin 併用 metformin,比起單用 metformin 的患者,更有效地降低 HbA1c4。在第24周時,不同劑量的 dapagliflozin 併用 metformi n降體重效果皆優於單用 metformin (p<0.0001),在空腹血糖值方面,dapagliflozin 併用 metformin 組都有明顯改善 (表二)。
表二 Dapagliflozin 臨床試驗結果4
Placebo group (n=137) |
Dapagliflozin 2.5 mg group (n=137) |
Dapagliflozin 5 mg group (n=137) |
Dapagliflozin 10 mg group (n=135) |
|
HbA1c at week 24 (%) |
||||
Change from baseline |
-0.30 |
-0.67 |
-0.70 |
-0.84 |
p value |
.. |
0.0002 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
Fasting plasma glucose at week 24 (mmol/L) |
||||
Change from baseline |
-0.33 |
-0.99 |
-1.19 |
-1.30 |
p value |
.. |
-0.0019 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
Total bodyweight at week 24 (kg) |
||||
Change from baseline |
-0.9 |
-2.2 |
-3.0 |
-2.9 |
p value |
.. |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
HbA at week 24 in patients with baseline HbA ≥9·0 (%) |
||||
Change from baseline |
-0.53 |
-1.21 |
-1.37 |
-1.32 |
p value |
.. |
NT |
-0.0068 |
-0.0290 |
NT=not tested under sequential testing procedure if previously tested endpoint was not statistically significant.
參、降血糖藥物之比較
一、新機轉降血糖藥物之比較
(一)DPP-4 inhibitors 與 GLP-1 receptor agonists 及 SGLT-2 inhibitor 之比較
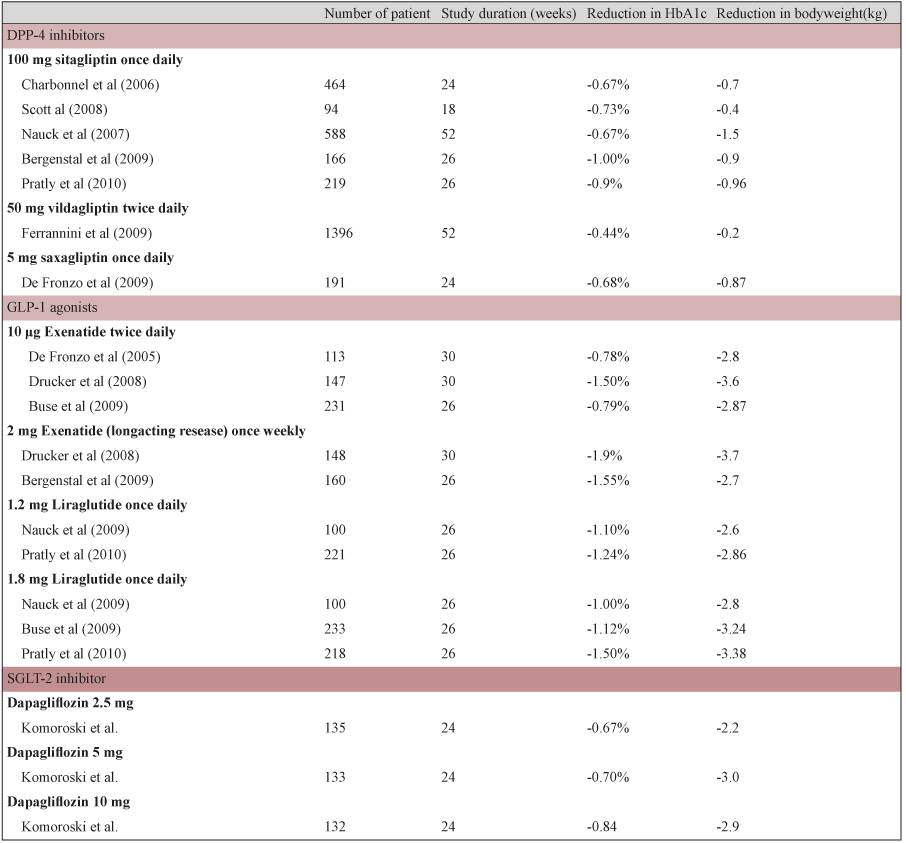
當併用 metformin 時,SGLT-2 inhibitor 降 HbA1c 的效果與 DPP-4 inhibitors 相似,但減輕體重的效果優於 DPP-4 inhibitors;GLP-1 receptor agonists 不論降低 HbA1c 或減輕體重的效果,皆優於 DPP-4 inhibitors。Richard Pratley 發表的一個26週,與 metformin 併用的研究指出,liraglutide (1.8 mg) 比起 sitagliptin,更有效改善血糖控制 (HbA1c -1.50% versus -0.90%,p<0.0001);一周注射一次2 mg Exenatide (長效劑型) 比起一天施打兩次的10 μg Exenatide,更為有效且耐受性更好;Liraglutide (1.8 mg) 減輕體重的表現比 sitagliptin 更好 (-3.38 kg versus -0.96 kg,p<0.0001);但 sitagliptin 在胃腸道的耐受性優於 Liraglutide,且 DPP-4 inhibitors 與 SGLT-2 inhibitor 皆為口服劑型,具備方便及經濟的好處4 (表三)。
表三 DPP-4 inhibitors vs GLP-1 receptor agonists vs SGLT-2 inhibitor之臨床試驗結果4,9
(二)GLP-1 類似物
1.Exenatide:
2005年在美國上市,為皮下注射劑型,目前有兩種劑量:10 μg 一天兩次;2 mg 長效型一星期一次。根據 AMIGO trial 收集1600 位16~75歲,以 metformin 或 sulfonylurea 或 metformin 加上 sulfonylurea 仍未達良好控制病人 (HbA1c 7.5%~11%),結果顯示不論原本使用 sulfonylurea、metformin 或 sulfonylurea 加上 metformin 的患者,併用 exenatide 可有效再降低 HbA1c,且在82周後仍能降低 HbA1c3。降低體重方面,約可降低 BMI 2~3左右,主要副作用為噁心及嘔吐、腹瀉等胃腸道不適症狀。
2.Liraglutide:
亦為皮下注射劑型,在 LEAD-6 試驗中,收納462位即使接受最大可耐受劑量的其他傳統降血糖藥,仍無法獲得良好控制的第二型糖尿病病人,隨機分派為加上 exenatide 或 liraglutide,直接比較兩者的有效性與安全性10。結果顯示 liraglutide 比 exenatide 更有效降低 HbA1c (-1.12% versus -0.79%,p<0.0001),腸胃道副作用也比較小 (2.5% versus 8.6%,p<0.0001) (表四)。但值得注意的是,Liraglutide 似乎有較高的胰臟炎風險,因此,有胰臟炎風險者不應給予本藥。
表四 比較 Exenatide 與 Liraglutide 的有效性與安全性10
Liraglutide |
Exenatide |
p value |
|
Half life (h) |
13 |
2 |
.. |
Frequency of injection |
0nce a day |
Twice a day |
|
Data from the LEAD-6 study |
|||
HbA1c (%) |
-1.12% |
-0.79% |
p<0.0001 |
Patients reaching HbA1c<7% |
54 |
43 |
p<0.0015 |
Fasting plasma glucose (mmol/L) |
-1.61 |
-0.6 |
p<0.0001 |
Hypoglycaemia |
1932 |
2600 |
p<0.0131 |
Patients with nausea at week 26 |
2.5% |
8.6% |
p<0.0001 |
Weight reduction (kg) |
-3.24 |
-2.87 |
NS |
HOMA-B (%) |
32.12 |
2.74 |
p<0.0001 |
HOMA-B=homoeostasis model of β-cell function |
|||
(三)傳統口服降血糖藥之比較
如表五所示,可依結構式的不同分為五大類,其中 metformin 及 sulfonylureas 降低HbA1c 效果最好且藥費便宜。Metformin 因為可減輕體重,為肥胖型 T2DM 首選藥物。Sulfonylureas 因為容易引起低血糖及體重增加,因此應小心使用於老人及肥胖病人。Thiazolidindione 好處是不易造成低血糖,但須注意可能引起水腫而加重心衰竭病人病情。Meglitinides 可有效降低飯後血糖值,但因其機轉亦為釋放胰島素,因此仍會使體重增加,但因為短效,故低血糖副作用較 sulfonylureas 低。Acarbose 也可有效降低飯後血糖值,但其胃腸道副作用常造成病人停藥。
表五 常用口服降血糖藥物治療結果11
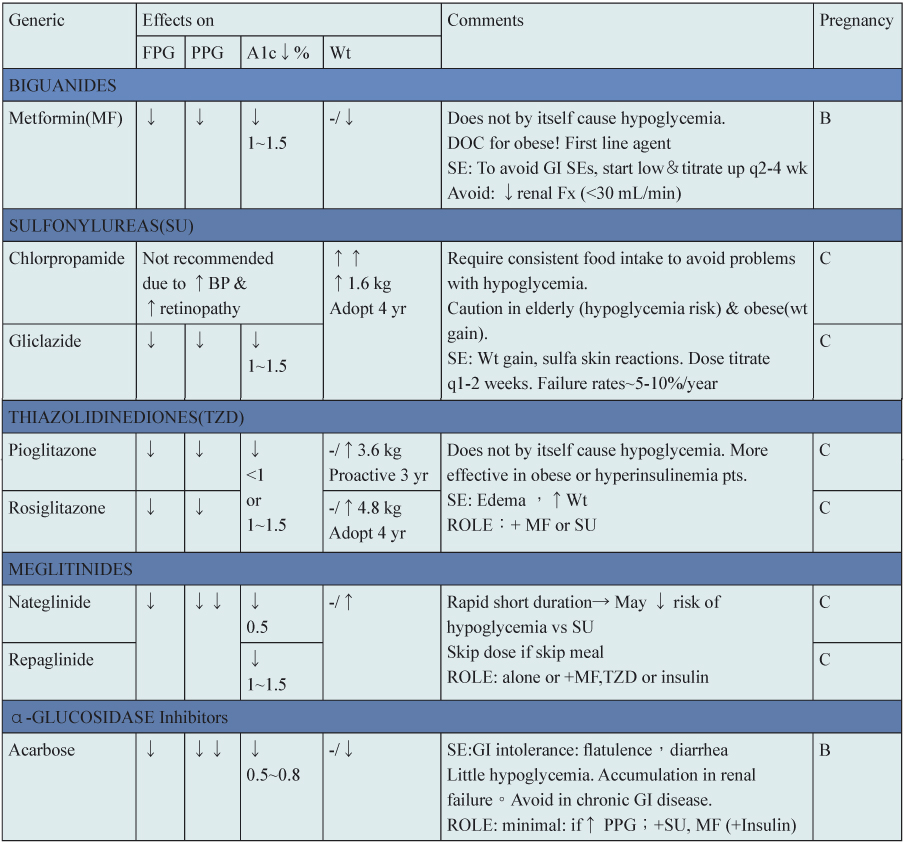
DOC=drug of choice BP=blood pressure Fx: function FPG=fasting plasma glucose
GI=gastrointestinal PPG=postprandial blood glucose SE=side effects Wt=weight
肆、結論
由於目前尚無明確證據證實某類藥物或某種藥物組合比其他藥物更能有效減少長期併發症,因此,治療效果仍以其降低血糖的能力而定。美國糖尿病學會與歐洲糖尿病研究學會提出治療流程,包括:(1) 在不造成血糖過低的情況下,儘可能將血糖控制於正常範圍內或盡量接近正常範圍 (HbA1c<7%),(2) 在診斷為糖尿病時,便應該開始生活型態調整,並開始使用 metformin,(3) 若未達成血糖目標值 (HbA1c>75),儘快加上其他藥物或換新的治療,(4) 口服藥物若未能達到目標,應盡早使用胰島素。
目前 T2DM 的治療仍有一半以上的病人,即使已用到最大劑量,還是無法控制血糖達到目標值。新一類機轉 SGLT-2 inhibitors 的出現希望能輔助其他降血糖藥物使病人達到良好血糖控制目標,或成為患者對其他降血糖藥品有使用禁忌或不耐受時的替代療法;但長期使用的安全性及效益尚待更大型且長期的臨床試驗的答案。
參考資料:
1. Nathan DM, Buse JB, Davidson MB, et al: Medical Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes: A Consensus Algorithm for the Initiation and Adjustment of Therapy: A consensus statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009;32:193-203.
2. Bergenstal RM, Wysham C, MacConell L, et al: Efficacy and safety of exenatide once weekly versus sitagliptin or pioglitazone as an adjunct to metformin for treatment of type 2 diabetes (DURATION-2): a randomised trial. The Lancet;In Press, Corrected Proof.
3. Tahrani AA, Piya MK, Kennedy A, Barnett AH. Glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes: Targets and new therapies. Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2010;125:328-61.
4. Bailey CJ, Gross JL, Pieters A, Bastien A, List JF. Effect of dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes who have inadequate glycaemic control with metformin: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. The Lancet 2010;375:2223-33.
5. Meier JJ, Gallwitz B, Nauck MA. Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 and Gastric Inhibitory Polypeptide: Potential Applications in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. BioDrugs 2003;17:93-102.
6. Jabbour SA, Goldstein BJ. Sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors: blocking renal tubular reabsorption of glucose to improve glycaemic control in patients with diabetes. International Journal of Clinical Practice 2008;62:1279-84.
7. Lee WS, Kanai Y, Wells RG, Hediger MA. The high affinity Na+/glucose cotransporter. Re-evaluation of function and distribution of expression. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1994;269:12032-9.
8. Idris I, Donnelly R. Sodium–glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors: an emerging new class of oral antidiabetic drug. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism 2009;11:79-88.
9. Scheen AJ, Radermecker RP. Addition of incretin therapy to metformin in type 2 diabetes. The Lancet 2010;375:1410-2.
10. De Block CEM, Van Gaal LF. GLP-1 receptor agonists for type 2 diabetes. The Lancet 2009;374:4-6.
11. Loren Regier,Brent Jensen.Oral hypoglycemic agents.RxFiles 7th Edition.
The New Drugs of Type 2 Diabetes and Comparison with the Other Existing Agents
Hui-min Chu
Department of Pharmacy, Chang Gung Medical Foundation. Yunlin Branch
Abstract
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and it's complications are always lower our quality of life and make a great burden to our society. Maintaining glycemic levels as close to the non-diabetic range as possible has been demonstrated to have a beneficial effect on diabetes-specific microvascular complications, including retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy. Recently, some drugs like dipeptidyl peptide-Ⅳ (DPP-4) inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists are based on mechanism of incretin; the former have lower effect in reducing HbA1c than other oral hypoglycemic agents, the latter have better effect in reducing HbA1c but they are administrated by injection. Now, the new drug: sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitor is in the phase 3 clinical trial, which can help to facilitate glucose elimination in urine. Due to the new mechanism, it may be useful in T2DM patients with little side effects in the future.

