摘要
脊髓側索硬化症 (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, ALS) 為一漸進性神經退化疾病,因侵犯大腦或是脊髓中的神經細胞,運動神經元漸進性退化而導致肌肉無力、失能甚至是死亡,病人平均存活時間約3-5年,危險因子為年紀和家族史。ALS 合併有上下運動神經元症狀,上運動神經元 (upper motor neuron, UMN) 因直接去神經化造成無力、萎縮和肌纖維自發性收縮的結果;而下運動神經元 (lower motor neuron, LMN) 則因脊髓神經側皮質退化造成反射過強和痙攣現象。2009年 AAN (American Academy of Neurology) 認為 riluzole 是種安全且有效藥品,以減緩 ALS 惡化程度為目的,建議 ALS 病人每日服用 riluzole 2次、每次50 mg,另外對於一些衍生出來的症狀處理,也可以減輕病人的不適。
關鍵字:脊髓側索硬化症、ALS、riluzole、amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
壹、前言1
脊髓側索硬化症 (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, ALS) 最早在1869年由 Charcot 所提出,也稱為 Lou Gehrig's disease (以紐約洋基隊棒球選手為名),為一漸進性神經退化疾病 (progressive neurodegenerative disease),因侵犯大腦或是脊髓中的神經細胞,運動神經元漸進性退化而導致肌肉無力、失能甚至是死亡,病人平均存活時間約3-5年。
貳、流行病學2
根據歐洲與北美在2007年的資料顯示,其發生率約1.47-2.7人/100,000/年,盛行率為2.7-7.4人/100,000/年。依中華民國運動神經元病友協會的統計資料顯示,目前台灣約有800多人罹病。依種族來看,高加索人種有較高的罹病率。年齡分布方面,在40歲之後會每十年逐漸上升,在70-80歲時達高峰,之後會逐年下降。65-70歲之前,以男性佔多數,70歲之後,則兩性趨向均等。危險因子的探討方面,年紀和家族史皆為可被確立的因素。
參、臨床表徵與診斷3
ALS 合併有上下運動神經元症狀,上運動神經元 (upper motor neuron, UMN) 因直接去神經化造成無力、萎縮和肌纖維自發性收縮的結果;而下運動神經元 (lower motor neuron, LMN) 則因脊髓神經側皮質退化造成反射過強和痙攣現象。ALS 臨床表徵依 E1 Escorial 全球聯邦神經學標準 (Revised E1 Escorial World Federation of Neurology criteria) 就 UMN 及 LMN 不同程度分為五個等級:臨床確診 ALS (clinically definite ALS)、臨床極可能 ALS (clinically probable ALS、臨床可能性-實驗數據證實 ALS (clinically probable-laboratory-supported ALS)、臨床可能的 ALS (clinically possible ALS) 和懷疑可能 ALS (clinically suspected ALS) 五種類型。
ALS 約80%的病人會有不對稱肢體無力表現,上肢開始的預兆通常為手部無力,可能會拿不住東西,或在從事精細動作時出現困難,像是寫字、打字、拉拉鍊或扣釦子,使日常生活執行活動時動作不靈敏。下肢肌無力可能伴隨痙攣性步態,平衡感差、自發性彎曲肌痙攣與踝關節抽搐影響步態。延髓症狀則以構音困難 (dysarthria) 和吞嚥困難 (dysphagia) 為代表,說話變慢,容易咳嗽或是嗆到。
疾病進展的模式,60-70%病人會由單側上肢或下肢進展到對側上下肢。另外,延髓開始的個案會傾向往上肢蔓延,然後到對側上肢。少部分 ALS 病人會產生漸進性吞嚥困難,增加吸入性肺炎的機率,必須以鼻胃管或是積極處理分泌物的方式處理;而較嚴重的漸進性神經肌肉呼吸衰竭,須以氣切或是終生使用呼吸器方式進行,最終常成為病人死亡的主因 (見圖一)。
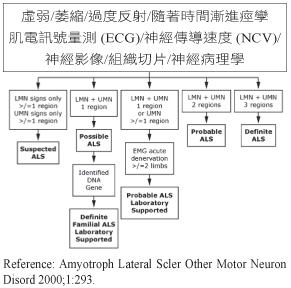
圖一 EI Escorial 脊髓側索硬化症臨床診斷摡圖
肆、藥品治療1,4
ALS 病理機轉呈現多重因子、基因因素及分子組成互相影響,包含過度氧化、傳達神經興奮毒性會興奮 glutamate 的釋放、粒線體功能失常、神經軸突傳導功能損害。Riluzole (2-aminobenzothiazole,商品名 Rilutek) 是唯一經美國食品藥物管理局 (FDA) 通過對 ALS 存活有影響力之藥品,可使 ALS 病人延長存活時間或延後使用機械呼吸器的時間。
2009年 AAN (American Academy of Neurology) 認為 riluzole 是種安全且有效藥品,以減緩 ALS 惡化程度為目的。AAN 提出 riluzole 的適應症如下:(一) E1-Escorial criteria 臨床確診 ALS (clinically definite ALS) 及臨床極可能 ALS (clinically probable ALS)。(二) 症狀持續少於五年。(三) 肺活量大於60%預測值。(四) 無氣切的病人。
Riluzole 的機轉如下:(一) 對 glutamate 的釋放具有抑制作用 (glutamate為造成神經元退化的因子)。(二) 電壓依賴型鈉離子通道的去活化作用。(三) 可能干擾神經傳導物質與興奮性胺基酸接受體之結合。
Riluzole 口服生體可用率約60%,血漿蛋白結合比率達96%,主要與白蛋白和脂蛋白結合,因此高脂肪食物會減低藥品吸收。藥品排除率半衰期為12小時,藉由 cytochrome P450 enzyme1A2 代謝,因此藥效可能被 CYP1A2 inhibitors 所影響:例如 theophylline 和 caffine 可能減少 riluzole 排除速率。Riluzole 建議劑量為每日服用兩次,每次50 mg,劑量增加其療效無相對的加強,反而副作用會增加。最常見的副作用包括衰弱無力 (15%-20%)、噁心 (12%-21%)、眩暈、胃腸疾病、肺功能減弱 (10%-16%) 和肝功能異常 (SGPT↑),嗜中性白血球減少症少見。Riluzole 會造成肝臟胺基轉移酵素上升,大致有一半接受 riluzole 治療的 ALS 病人會出現麩丙酮酸轉胺脢 (ALT) 超過正常值上限 (upper limit of normal, ULN) 的情形,8%病人增加至3倍 ULN,2%增加5倍 ULN。因此 riluzole 治療前3個月每個月必須作肝功能檢查,之後每三個月做一次。
伍、結論4
針對 ALS 藥品控制治療療效受限,riluzole 是唯一對存活率有影響的藥品,且可以減緩 ALS 的惡化程度。建議 ALS 病人每日服用 riluzole 2次、每次50 mg,一般而言對於症狀持續小於5年,或肺活量達60%預測值,或無氣切患者使用 riluzole 較有效果,另外對於一些衍生出來的症狀處理用藥,也可以減輕病人的不適 (表一)。
表一 脊髓側索硬化症病人症狀治療用藥4
Symptom |
Medication |
Dosage |
Sialorrhoea |
Amitriptyline |
12.5-125 mg hs |
Atropine sulphate |
0.4 mg q4-6h 1-2 ophthalmic drops SL q4-6h |
|
Glycopyrrotate |
1-2 mg tid |
|
Hyoscyamine sulphate |
0.125-0.25 mg q4h |
|
Sialorrhoea |
Diphenhydramine |
25-50 mg tid |
Scopolamine transdermal patch |
0.5 mg behind ear q72h |
|
Emotional lability / pseudobulabar affect |
Dextromethorphan/quinidine |
20 mg/10 mg bid |
Amitriptyline |
12.5-125 mg hs |
|
SSRI antidepressants |
20-100 mg qd |
|
Mirtazapine |
15-30 mg hs |
|
Venlafaxien |
37.5-75 mg bid-tid |
|
Fatigue |
Amantadine |
100 mg AM, Noon |
Modafinil |
100-200 mg qAM |
|
Pemoline |
18.75-93.75 mg qd |
|
Bupropion SR |
150-450 mg qd |
|
Fluoxetine |
20-80 mg qd |
|
Venlafaxine |
75-225 mg qd |
|
Methylphenidate |
10 mg bid-tid |
|
Pyridostigmine |
60 mg tid |
|
Depression |
Mirtazapine |
15-30 mg hs |
SSRI antidepressants |
20-100 mg qd |
|
TCAs |
20-150 mg qd |
|
Venlafaxine |
37.5-75 mg qd |
|
Anxiety |
Diazepam |
2-10 mg tid |
Lorazepam |
0.5-2 mg bid-tid |
|
Buspirone |
10 mg tid |
|
SSRI antidepressants |
10-100 mg qd |
|
Mirtazapine |
15-30 mg hs |
|
Spasticity |
Baclofen |
10-60 mg tid |
Dantrolene |
25-100 mg tid-qid |
|
Tizanidine |
2-9 mg qid |
|
Benzodiazepines |
2-10 mg tid |
|
Cramps |
Vitamin E |
400 IU tid |
Phenytoin |
300 mg hs |
|
Diazepam |
2-10 mg tid |
|
Urinary urgency |
Oxybutynin |
2.5-5 mg bid |
Amitriptyline |
12.5-75 mg hs |
|
Tolterodine |
1-2 mg bid |
|
Oxybutynin patches |
3.9 mg qd |
|
Impaired sleep |
Zolpidem |
5-10 mg hs |
Zaleplon |
5-10 mg hs |
|
Amitriptyline |
12.5-125 mg hs |
|
Mirtazapine |
10-30 mg hs |
|
Impaired sleep |
Temazepam |
7.5-30 mg hs |
Chloral hydrate |
500-10000 mg hs |
|
Constipation |
Docusate |
240 mg qd |
Magnesium hydroxide |
30-60 mL prn |
|
Bisacodyl |
10-15 mL prn |
|
Lactulose |
15-30 mg qd |
|
Magnesium citrate |
75-150 mL bid |
|
SL = sublingual; SR = slow release; SSRI = selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; TCAs = tricyclic antidepressants |
||
參考資料:
1. Cheah BC, Vucic S, Krishnan AV, Kiernan MC: Riluzole, neuroprotection and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Curr Med Chem 2010;17(18):1942-199. Review.
2. Worms PM: The epidemiology of motor neuron diseases: a review of recent studies. J Neurol Sci 2001; 191:3.
3. Brooks BR, et al: EI Escorial revisited: revised criteria for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord. (2000)
4. Gordon PH, et al: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: pathophysiology, diagnosis and management. CNS Drugs 2011 Jan;25(1):1-15.
Drug Therapy for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Hsiao Jui-Lan1, Lee Yen-Jung2, Chen Tsung-Hsien1, Tu Shu-Chien1, Yu Cheng-Ying1
Department of Pharmacy, Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital1
Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Kaohsiung Municipal Ta-Tung Hospital2
Abstract
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that causes muscle weakness, disability, and eventually death, with a median survival of three to five years.
The hallmark of ALS is the combination of upper motor neuron (UMN) and lower motor neuron (LMN) involvement. Riluzole is the only drug to have any impact on survival in ALS. A 2009 American Academy of Neurology (AAN) practice parameter concluded that riluzole is safe and effective for slowing ALS progression to a modest degree. The recommended dosage of riluzole is 50 mg twice daily. Many agents may help therapies for ALS Symptom management.

