摘要
MRSA遍佈醫院及社區,為近年來極被注意的一種致病菌。MRSA 的感染會導致患者的住院天數延長及醫療費用增加。近年來亦發現 MRSA 對 vancomycin 感受性降低,甚至已有產生抗藥性的菌株 (VRSA) 被報告。
本案例為一已接受定期血液透析治療的紅斑性狼瘡患者,因突然意識不清住院,住院後診斷為左側髖部敗血性關節炎合併血液培養報告為 MRSA。在接受 vancomycin 1 g 一星期兩次治療時,測得波谷值為14.02 mg/L,低於目標波谷值15-20 mg/L,且 MIC 爬升至2 mcg/mL;後改成 daptomycin 500 mg/vial 每2天1支,daptomycin 之 MIC 亦上升至3 mcg/mL;因此改成 linezolid 600 mg 每12小時一支合併 sodium fusidate 500 mg 每天三次,經治療18天後,血液培養報告已無 MRSA。此案例的 vancomycin 治療失敗除了劑量不適當,MIC 慢慢爬升導致抗藥性亦是原因之一。
關鍵字: 萬古黴素、抗藥性金黃色葡萄球菌、波谷值、vancomycin、MRSA、Trough level
壹、前言
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) 之定義為對 oxacillin 之最小抑菌濃度 (minimal inhibitory concentration,MIC) ≥ 4 mcg/mL 的金黃色葡萄球菌感染。依感染來源分為與住院有關的感染 (Health care–associated MRSA)、來自社區的感染(Community-associated MRSA) 及住院三天內發生,但感染來自先前社區的感染 (Health care–associated community-onset MRSA)。MRSA 感染一般會使用 vancomycin 治療,但目前已發現具 vancomycin 抗藥性的葡萄球菌。
MRSA 引起之肺炎 (pneumonia),經驗療法須考慮是否為嚴重的社區型肺炎,藥物治療以 vancomycin 為主,然而失敗率卻很高,因 vancomycin 很少滲透進入肺組織1;替代治療為 linezolid,早晚口服或注射600 mg,linezolid 在肺組織的濃度遠高於血漿、巨噬細胞與支氣管黏膜的濃度2;然而若併發氣胸,則需引流並配合抗生素治療。
當 MRSA 導致菌血症 (bacteremia) 及心內膜炎 (endocarditis) 時,建議以 vancomycin 15-20 mg/kg/dose 每8-12小時靜脈滴注3;另可考慮 daptomycin 6 mg/kg/dose 每24小時靜脈注射,或較高劑量8-10 mg/kg/dose4;臨床上使用 vancomycin 時,不建議併用gentamicin,因會增加腎毒性5;亦不建議使用 vancomycin 時,再併用 rifampin,因為臨床上不但沒有益處,反而會增加肝毒性、藥物間交互作用與抗藥性6;但若是人工瓣膜引起的心內膜炎,則建議併用 vancomycin 與 rifampin 每8小時給予300 mg,至少 6 週,且前2週合併 gentamicin 1 mg/kg/dose 每8小時靜脈注射3。
對於 MRSA 導致之骨頭及關節感染,若已產生膿瘍,手術清瘡與引流是必要的;雖在動物試驗中發現 vancomycin 對骨頭滲透性很差,但仍以 vancomycin 為主要的治療7;有專家建議加上 rifampin 每天600 mg 或300-450 mg 一天兩次,因 rifampin 對骨頭與生物膜滲透性佳8。Daptomycin 是非經腸胃道的替代藥品,臨床發現6 mg/kg/day 效果最好9;以 daptomycin 治療時,須考慮 MIC 慢慢爬升引起治療失敗,亦得小心引起橫紋肌溶解之風險。另一個替代藥品為 linezolid,它在發炎骨頭中的濃度極高,當使用超過2週時,建議每週追蹤全血球計數 (complete blood counts),以防骨髓抑制產生;使用超過1個月,須安排眼科理學檢查,預防視神經炎發生10。
Vancomycin 之治療範圍很狹窄,劑量太高易引起腎及耳毒性之危險,劑量太低則導致治療失敗與藥物抗藥性11。Vancomycin 之療效則依據24小時區域下面積除以最小抑菌濃度 (AUC/MIC),若是臨床上痊癒,數值須 > 400,若要達到微生物治癒,數值須 > 85012,13。對於透析的病人,vancomycin 之維持劑量取決於透析前波谷值、淨體重與下次透析期間的狀況11,因 vancomycin 具有高變異性之3階段藥物動力學 (3-phasic pharmacokinetic)14,因此建議在每次透析前先測波谷值,以決定 vancomycin 之劑量。
貳、案例報告
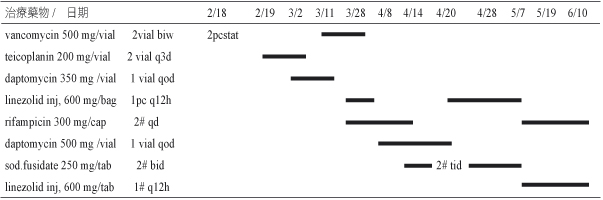
個案為26歲的女性病人,先天雙盲,身高152公分、體重42.6公斤,BMI 值為18.4,於2008年確診為紅斑性狼瘡 (systemic lupus erythematosus,SLE),長期以 methylprednisolone 4 mg/tab 早晚飯後1顆來控制。個案同時有癲癇病史多年,自2004年起以口服抗癲癇藥控制。2008年診斷出慢性腎衰竭,於 2010年3月起接受每週三次血液透析治療。2011年2月9日因突然意識不清而到本院急診就診,當時沒有發燒、顫抖、嘔吐或胸痛,但有抽搐情形發生。胸部X光發現有心臟肥大、左下肺葉有浸潤情形。患者之檢驗數值異常如下:Cr 2.97 mg/dL; CRP 42.0 mg/L; hemoglobin 7.5 g/dL; platelets 111×1000/uL。臨床臆診為頑固型癲癇、全身性紅斑狼瘡及慢性腎疾病,隨即安排到病房接受進一步診察與治療。當時的藥物治療為 methylprednisolone 4 mg/tab 早晚飯後1顆、carbamazepine CR 200 mg/tab 早晚飯後3顆、phenytoin sodium 100 mg/cap 早晚飯後2顆、topiramate 100 mg/tab 早上飯後1顆、晚上飯後2顆。住院後第9天,病人發燒至38.3℃,血液學檢查呈現有白血球增多症,胸部X光檢查亦發現有胸腔積水 (pleural effusion);先給予 ceftriaxone 1 gm 每12小時1支,2月18日血液培養報告為 MRSA,且 vancomycin 的 MIC < 0.5 mcg/mL,抗生素治療改為 vancomycin 1 g 每週兩次,並移除身上不必要之導管,同時置換中央靜脈導管,此外,安排心臟超音波,並排除心內膜炎所引起。直到3月2日,病人仍高燒至38.3℃,將抗生素更換成 daptomycin 350 mg/vial 每2天1支;3月9日病人抱怨左髖部疼痛;3月11日血液培養報告為MRSA,且 vancomycin 的 MIC 為1.0 mcg/mL,將抗生素換回 vancomycin 1 g 每週兩次;3月18日測 vancomycin 波谷 (trough) 值為14.02 mg/L;3月23日血液培養報告仍為 MRSA,且 vancomycin 的 MIC 爬升至2.0 mcg/mL,daptomycin 的 MIC 為2.0 mcg/mL;3月26日測 vancomycin 波峰 (peak) 值為17.17 mg/L;因此自3月28日,改成 linezolid inj 600 mg/bag 每12小時1支,與 rifampicin 300 mg/cap 早上飯後2顆;4月8日將 linezolid inj 600 mg/bag 換成 daptomycin 500 mg/vial 每2天1支繼續治療;於4月14日以 sod.fusidate 250 mg/tab 早晚飯後2顆取代 rifampicin。此外,病人的骨骼掃描 (bone scan) 與髖部核磁共振攝影 (MRI),證實左髖部有多處壞死,為敗血性關節炎 (septic arthritis);4月16日血液培養報告依舊為 MRSA,且 vancomycin 的 MIC 仍為2.0 mcg/mL,daptomycin 的 MIC 已上升至3.0 mcg/mL,進而又將 daptomycin 500 mg/vial 換回 linezolid inj 600 mg/bag 每12小時1支,sod.fusidate 250 mg/tab 劑量增加至三餐飯後2顆;4月26日因懷疑有兩種不同型態 MRSA 菌株感染,因而血液培養兩組,結果 MIC 分別為 vancomycin 2.0、2.0 mcg/mL,daptomycin 3.0、6.0 mcg/mL;然而自4月27日又連續三天發燒,但仍維持原抗生素治療,直至5月7日,血液培養報告已無任何細菌生長,左髖關節活動亦較自如。
病人於使用抗生素期間之相關治療藥品請參見表一;治療期間之檢驗數值請參見表二;治療期間 vancomycin 與 daptomycin 之 MIC 變化如圖一。
表一 藥物治療史
表二 檢驗數值總表
A. 生化檢驗數值
項目/日期 |
單位 |
2/9 |
2/11 |
2/14 |
2/17 |
2/18 |
2/19 |
2/21 |
2/22 |
2/24 |
3/1 |
3/8 |
3/18 |
3/26 |
3/29 |
4/2 |
4/8 |
4/12 |
4/15 |
4/19 |
eGFR |
mL/min/1.73㎡ |
19 |
17 |
16 |
20 |
27 |
18 |
14 |
||||||||||||
BUN |
mg/dL |
47 |
58 |
53 |
40 |
56 |
47 |
74 |
||||||||||||
creatinine |
mg/dL |
2.97 |
3.20 |
3.37 |
2.88 |
2.20 |
3.11 |
3.95 |
||||||||||||
ALT/GPT |
U/L |
47 |
48 |
52 |
54 |
60 |
49 |
34 |
20 |
26 |
61 |
41 |
52 |
31 |
||||||
Na |
meq/L |
136 |
137 |
133 |
141 |
140 |
139 |
135 |
134 |
120 |
121 |
119 |
125 |
126 |
128 |
|||||
K |
meq/L |
4.2 |
3.9 |
3.9 |
3.9 |
3.1 |
4.4 |
3.6 |
4.4 |
5.2 |
3.9 |
4.3 |
3.6 |
2.9 |
2.5 |
|||||
Ca |
mg/dL |
8.0 |
6.9 |
7.4 |
7.8 |
8.3 |
||||||||||||||
P |
mg/dL |
5.6 |
7.8 |
8.3 |
7.5 |
2.3 |
||||||||||||||
albumin |
g/dL |
1.2 |
1.2 |
1.2 |
1.4 |
1.8 |
1.8 |
1.8 |
||||||||||||
CRP |
mg/L |
42 |
56.7 |
58.7 |
218.1 |
233.9 |
96.3 |
75.5 |
34.9 |
42.5 |
B. 血液學檢驗數值
項目/日期 |
單位 |
2/9 |
2/11 |
2/14 |
2/17 |
2/18 |
2/19 |
2/21 |
2/22 |
2/24 |
3/1 |
3/8 |
3/18 |
3/26 |
3/29 |
4/2 |
4/8 |
4/12 |
4/15 |
4/19 |
WBC |
1000/µL |
6.3 |
6.5 |
12.4 |
11.2 |
8.3 |
5.6 |
4.8 |
5.1 |
4.3 |
5.8 |
3.8 |
2.5 |
3.2 |
2.5 |
|||||
RBC |
million/µL |
2.44 |
3.34 |
2.95 |
2.64 |
2.80 |
3.31 |
2.47 |
2.02 |
4.13 |
3.43 |
2.89 |
2.34 |
3.47 |
2.20 |
|||||
hemoglobin |
g/dL |
7.5 |
11.2 |
9.3 |
8.2 |
7.4 |
8.0 |
9.4 |
7.0 |
5.9 |
11.8 |
10.2 |
8.4 |
6.8 |
10.4 |
6.5 |
||||
platelets |
1000/µL |
111 |
109 |
120 |
122 |
89 |
86 |
77 |
60 |
145 |
157 |
219 |
159 |
62 |
45 |
96 |
||||
segment |
% |
86.0 |
75.3 |
91.0 |
90.0 |
93.0 |
85.5 |
77.0 |
69.0 |
71.0 |
79.2 |
78.8 |
68.0 |
80.7 |
77.0 |
|||||
band |
% |
2.0 |
2.0 |
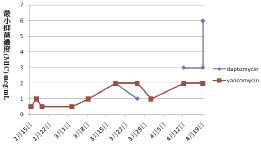
圖一 Vancomycin 與 daptomycin 在治療期間之 MIC 變化
參、討論
本案例為全身性紅斑狼瘡患者,因免疫功能低下易導致感染,使用抗生素期間,又因產生抗藥性而導致治療失敗。首先給予 vancomycin 時,雖有給負載劑量1 g (即42 kg X 20-25 mg/kg),但測波谷濃度時未達穩定狀態 (steady state),測得波谷值為14.02 mg/L,比起目標波谷值15-20 mg/L 較低,顯示劑量不足,導致抗藥性治療失敗。建議 vancomycin 每星期給予2次,劑量增加至1250 mg,以達預測波谷值為17.53 mg/L。另外,vancomycin MIC 已爬升至2.0 mcg/mL 時,不適合再繼續使用,應立即改藥。此病人住院中反覆性發燒,主要是因為未及時發現左髖部敗血性關節炎;直至3月9日病人抱怨左髖部疼痛,醫師才發現左髖部有多處壞死,為敗血性關節炎,且3月11日血液培養報告亦為 MRSA,及時針對左髖部敗血性關節炎之 MRSA 做治療,對於 MRSA 導致之骨頭及關節感染,若已產生膿瘍,手術清瘡與引流是必要的,但家屬考慮許久,仍不接受手術清瘡,因而加上 rifampin 每天600 mg 或300-450 mg 一天兩次,因 rifampin 對骨頭與生物膜滲透性佳,此外以 linezolid 600 mg 每12小時一次替代 vancomycin,它在發炎骨頭中的濃度極高,兩種藥品併用4至6周,並隨時監測 CRP、WBC、segment、band 及血液 culcure 等,直到血液培養報告已無任何細菌生長,左髖關節活動亦較自如才停止治療。MRSA 之治療藥物表請參見表三。
表三 MRSA 之治療藥物表3
疾病 |
治療藥物 |
劑量 |
|
skin and soft-tissue infection (SSTI) |
purulent cellulitis |
clindamycin |
300-450 mg tid |
TMP-SMX |
1-2 DS bid |
||
doxycycline |
100 mg bid |
||
minocycline |
200 mg 3 1, then 100 mg bid |
||
linezolid |
600 mg bid |
||
nonpurulent cellulitis |
β-lactam (eg, cephalexin and dicloxacillin) |
500 mg qid |
|
clindamycin |
300-450 mg tid |
||
β-lactam (eg, amoxicillin) and/or TMP-SMX or a tetracycline |
Amoxicillin: 500 mg tid See above for TMP-SMX and tetracycline dosing |
||
linezolid |
600 mg bid |
||
complicated SSTI |
vancomycin |
15-20 mg/kg/dose iv q 8-12 h |
|
linezolid |
600 mg po/iv bid |
||
daptomycin |
4 mg/kg/dose iv qd |
||
telavancin |
10 mg/kg/dose iv qd |
||
clindamycin |
600 mg po/iv tid |
||
bacteremia and infective endocarditis |
bacteremia |
vancomycin |
15-20 mg/kg/dose iv q 8-12 h |
daptomycin |
6 mg/kg/dose iv qd |
||
infective endocarditis, prosthetic valve |
vancomycin and gentamicin and rifampin |
15-20 mg/kg/dose iv q 8-12 h 1 mg/kg/dose iv q 8 h 300 mg po/iv q 8 h |
|
pneumonia |
pneumonia |
vancomycin |
15-20 mg/kg/dose iv q 8-12 h |
linezolid |
600 mg po/iv bid |
||
clindamycin |
600 mg po/iv tid |
||
bone and joint infections |
osteomyelitis |
vancomycin |
15-20 mg/kg/dose iv q 8-12 h |
daptomycin |
6 mg/kg/day iv qd |
||
linezolid |
600 mg po/iv bid |
||
clindamycin |
600 mg po/iv tid |
||
TMP-SMX and rifampin |
3.5-4.0 mg/kg/dose po/iv q 8-12 h 600 mg po qd |
||
septic arthritis |
vancomycin |
15-20 mg/kg/dose iv q 8-12 h |
|
daptomycin |
6 mg/kg/day iv qd |
||
linezolid |
600 mg po/iv bid |
||
clindamycin |
600 mg po/iv tid |
||
TMP-SMX |
3.5-4.0 mg/kg/dose po/iv q 8-12 h |
||
肆、結論
選擇藥品時,劑量需足夠以達治療血中濃度目標,同時需考慮藥品本身的特性,及可能會引起之副作用。當選擇 vancomycin 時,負載劑量為20-25 mg/kg,最大輸注速率為15 mg/min,且須小心 MIC 會慢慢爬升,導致抗藥性治療失敗,在給予第4至5個劑量後,建議在每次透析前監測血中濃度,目標波谷值為15-20 mg/L,以確保治療效果。此案例的 vancomycin 治療失敗除了劑量不適當,MIC 慢慢爬升導致抗藥性亦是原因之一。因此在臨床藥品使用上,給予足夠劑量來治療 MRSA 是相當重要的。
參考資料:
1. Cruciani M, Gatti G, Lazzarini L, et al: Penetration of vancomycin into human lung tissue. J Antimicrob Chemother 1996; 38: 865-9.
2. Conte JE Jr., Golden JA, Kipps J, et al: Intrapulmonary pharmacokinetics of linezolid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2002; 46: 1475-80.
3. Catherine Liu, Arnold Bayer, Sara E. Cosgrove, et al: Clinical practice guidelines by the infectious diseases society of America for the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in adults and children. CID 2011; 52: 1-38.
4. Vance G. Fowler, Jr., M.D., M.H.S., Helen W. Boucher, M.D., G. Ralph Corey, M.D., et al: Daptomycin versus Standard Therapy for Bacteremia and Endocarditis Caused by Staphylococcus aureus. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 653-65.
5. Cosgrove SE, Vigliani GA, Fowler VG Jr., et al: Initial low-dose gentamicin for Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia and endocarditis is nephrotoxic. Clin Infect Dis 2009; 48: 713-21.
6. Riedel DJ, Weekes E, Forrest GN. Addition of rifampin to standard therapy for treatment of native valve infective endocarditis caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2008; 52: 2463-7.
7. Sia IG, Berbari EF. Infection and musculoskeletal conditions: osteomyelitis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 2006; 20: 1065-81.
8. Darley ES, MacGowan AP. Antibiotic treatment of grampositive bone and joint infections. J Antimicrob Chemother 2004; 53: 928-35.
9. Crompton JA, North DS, McConnell SA, et al: Safety and efficacy of daptomycin in the treatment of osteomyelitis: results from the CORE Registry. J Chemother 2009; 21: 414–20.
10. Rayner CR, Baddour LM, Birmingham MC, et al: Linezolid in the treatment of osteomyelitis: results of compassionate use experience. Infection 2004; 32: 8-14.
11. Vandecasteele SJ, De Bacquer D, De Vriese AS. Implementation of a dose calculator for vancomycin to achieve target trough levels of 15-20 μg/mL in persons undergoing hemodialysis. Clin Infect Dis 2011; 53(2): 124-9.
12. Rybak M, Lomaestro B, Rotschafer JC, et al: Therapeutic monitoring of vancomycin in adult patients: a consensus review of the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, the Infectious Diseases Society of America, and the Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists. Am J Health Syst Pharm 2009; 66(1): 82-98.
13. Moise-Broder PA, Forrest A, Birmingham MC, et al: Pharmacodynamics of vancomycin and other antimicrobials in patients with Staphylococcus aureus lower respiratory tract infections. Clin Pharmacokinet 2004; 43(13): 925-42.
14. Vandecasteele SJ, De Vriese AS. Vancomycin dosing in patients on intermittent hemodialysis. Semin Dial 2011; 24(1): 50-5.
Vancomycin Minimal Inhibitory Concentration Elevated in a MRSA Patient
Chiu-Ju Chen1, Yi-Ping Hsiang1, Ping-Yu Lee1, Yih-Dih Cheng2, Chih-Hsiung Lee3
Department of Pharmacy, Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital1
Department of Pharmacy, China Medical University Hospital2
Department of Internal Medicine Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital3
Abstract
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is one of the noticeable pathogen and proliferates in the hospital and the community. MRSA may cause long hospital stay and high medical cost. MRSA reduced susceptibities to vancomycin as vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA) recently.
Here presented a 26-year-old female in-patient with a medical history of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) underwent hemodialysis for acute disturbance of consciousness. The diagnosis of septic arthritis with the MRSA (+) blood culture was reported after hospitalization. Initially, she was treated with vancomycin 1 g intravenous (IV) twice a week. The vancomycin trough level revealed 14.02 mg/L that was below target level 15 mg/L and minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) elevated to 2 mcg/mL. When vancomycin shifted to daptomycin, MIC of daptomycin elevated to 3 mcg/mL. The combination therapy with linezolid 600 mg IV every 12 hours and sodium fusidate 500 mg orally three times a day were prescribed. After 18 day-treatment, there was no more MRSA (+) blood culture. The initial vancomycin treatment failure would be due to inappropriateness of dosing and MIC creeps among MRSA susceptible strains. Therefore, the appropriate vancomycin dosing for treating MRSA is important.

