摘要
Penicillin (PEN) 和 cephalosporin (CEPH) 引起嚴重立即型過敏反應 (anaphylaxis) 的發生率極低。PEN 和 CEPH 分子結構中造成過敏的主因是來自側鏈,而非 β-lactam 環。研究指出有 PEN 過敏史的病人其中高達90%之後仍可安全地再次使用 PEN,其原因是絕大部份的病人並不是真正對 PEN 過敏,即 IgE 媒介的過敏反應,例如蕁麻疹、血管性水腫、呼吸道痙攣、低血壓等。Penicillin 皮膚敏感試驗 (penicillin skin test,PST) 是評估 IgE 媒介之 PEN 過敏反應最值得信賴的方法,然而現況使用稀釋的 penicillin G 來進行 PST,其結果只能作為參考,不可盡信。PEN 和 CEPH 的交叉過敏率約1%,若經證實確定是 PEN 過敏者則其交叉過敏率為2.55%。PEN 過敏病人若要使用 CEPH,建議使用第三、四代 CEPH 或是選擇和原先引起過敏的 PEN 不同側鏈的 CEPH。對於之前使用 PEN 或 CEPH 導致過敏者,若有需要仍可謹慎使用不同側鏈的 PEN 或 CEPH。
關鍵字: 過敏、penicillin、cephalosporin、allergy
壹、前言
β-lactam 抗生素中最容易產生藥物過敏的是 penicillin (以下簡稱 PEN) 和cephalosporin (以下簡稱 CEPH)。約10%住院病人被報導對 PEN 過敏1,而 CEPH 過敏發生率低,約1%2。兩者之過敏反應可能是給藥後立刻發生,即立即型過敏反應,例如蕁麻疹 (urticaria);但也可能是使用數日甚至數週後才發生,即延遲型過敏反應,例如斑丘疹 (maculopapular exanthema,簡稱 MPE)。其過敏症狀可從輕微的皮膚局部紅疹到具有生命威脅的呼吸困難、休克、毒性表皮壞死溶解症 (toxic epidermal necrolysis,簡稱 TEN) 之嚴重過敏反應。本文將探討 PEN 和 CEPH 過敏及其交叉過敏 (cross allergy) 的真因,同時也提供相關的臨床建議。
貳、 PEN 和 CEPH 的嚴重立即型過敏反應
Anaphylaxis 是急性嚴重過敏反應,病人可能會出現呼吸道痙攣、低血壓甚至死亡,其機轉大部份和 IgE 相關3。PEN 和 CEPH 引起 anaphylaxis 的發生率極低,PEN 為0.004%-0.015%,CEPH 為0.0001%-0.1%4。資料顯示 PEN 過敏者相較於無過敏者反而比較不會發生 CEPH anaphylaxis,此結果倒是令人感到意外4。換言之,PEN 過敏者仍可謹慎使用 CEPH;而沒有 PEN 過敏者也不能保證使用 CEPH 絕對安全。
參、Penicillin 藥物過敏
PEN 分子結構中造成過敏的主因是來自側鏈 (R),而非 β-lactam 環 (圖一) 2,4。但要注意這只是主因,並不是絕對的,也就是說 β-lactam 環也可能是造成 PEN 過敏的原因。若過敏原因來自側鏈,則選擇不同側鏈的 PEN 應可避免過敏發生;但若過敏原因來自 β-lactam 環,則對所有的 PEN 和 CEPH 皆過敏,這是因為 PEN 和 CEPH 皆含有 β-lactam 環。PEN 中 ampicillin、amoxicillin、piperacillin 其側鏈類似,它們皆屬於 aminopenicillin,因此若對其中一個藥過敏,則應避免使用另外兩個藥。以上三者的複方藥 Unasyn 即 ampicillin-sulbactam、Augmentin 即 amoxicillin-clavulanate、Tazocin 即 piperacillin-tazobactam 也是如此。研究指出有 PEN 過敏史的病人其中高達90%之後仍可耐受 PEN 再次使用5,6。換言之,PEN 過敏者可能絕大部份並不是真正對 PEN 過敏。因為真正的 PEN 過敏是由 IgE 媒介的過敏反應,例如蕁麻疹、血管性水腫、呼吸道痙攣、過敏性休克等7。一旦發生以上過敏反應,若再次使用 PEN 則可能會有生命危險,故一般建議不要進行再激發試驗 (rechallenge)。
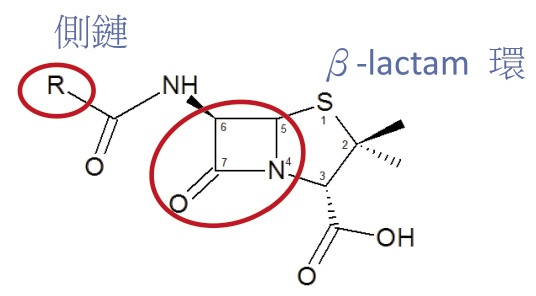
圖一 Penicillin 分子結構
肆、 Penicillin 皮膚敏感試驗 (penicillin skin test;PST)
PST 是評估 IgE 媒介之 PEN 過敏反應最值得信賴的方法。PST 使用的試劑,理想上應包括主要抗原決定化合物 benzylpenicilloyl 和次要抗原決定化合物 benzylpenicilloate、benzylpenilloate,而不單是稀釋的 penicillin G2,4。理想試劑的陰性預測值 (negative predictive value) 為100%,陽性預測值 (positive predictive value) 為40-100%2;至於使用稀釋的 penicillin G 來進行 PST 則無從知曉以上數值。
伍、Cephalosporin 藥物過敏
如同 PEN,CEPH 之所以過敏主要亦是取決於側鏈 R1 (不是 R2) (圖二) 2,4。其中 cefaclor、cephalexin、cefadroxil、cephradine、cefuroxime 其側鏈 R1雷同或類似,故屬同一群組,病人對該群組內某一個藥品過敏,則很有可能會對同群組內其他藥品過敏,即所謂「交叉過敏 (cross allergy)」4,8。又 cefepime、cefotaxime、ceftriaxone、ceftazidime、cefixime 亦屬同一群組4。而 cefazolin、flomoxef 則各自獨立自成一組4。若過敏來自某一群組中藥物,下次可選擇不同群組的 CEPH 應可避免過敏發生,除非過敏原因來自 β-lactam 環。
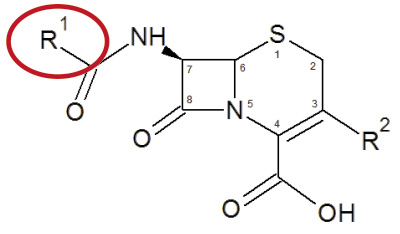
圖二 Cephalosporin 分子結構
陸、PEN 過敏病人可否使用 CEPH?
長久以來一直有迷思認為 PEN 過敏者,若之後使用 CEPH 將會引發交叉過敏,其機率可達10%9。然而,經由審慎的文獻回顧發現情形並不是如此:整體來看,PEN 和 CEPH 的交叉過敏率約1%,若經證實確定是 PEN 過敏者則其交叉過敏率為2.55%10。研究亦發現 PEN 過敏者使用第一代 CEPH: cefazolin、cefadroxil、cephalexin、cephradine 等的交叉過敏風險最高 (odds ratio 4.8;95%信賴區間3.7-6.2),使用第二代 CEPH:cefaclor、cefuroxime 等的交叉過敏風險則微不足道 (odds ratio 1.1;95%信賴區間0.6-2.1),而第三、四代 CEPH:ceftriaxone、ceftazidime、cefepime 等則與 PEN 無交叉過敏風險10。值得一提的是 amoxicillin 過敏者使用 cefadroxil 的交叉過敏機率高達27%11,是文獻中看到的最高值,可能是因為兩者有完全相同的側鏈所致 (圖三)。因此 PEN 過敏病人若要使用 CEPH,建議使用第三、四代 CEPH 或是選擇和原先引起過敏的 PEN 不同側鏈的 CEPH10。
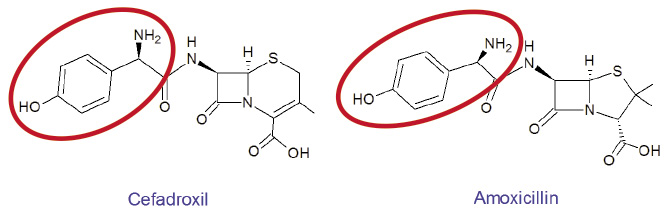
圖三 Cefadroxil 和 Amoxicillin 有完全相同的側鏈
柒、CEPH 過敏病人可否使用 PEN?
由於 cefadroxil、cephalexin、cephradine、cefaclor 的側鏈和 amoxicillin、ampicillin 的側鏈雷同或極類似,因此若病人對上述 CEPH 過敏,則不建議使用 amoxicillin、ampicillin,即使 PST 的結果是陰性反應也是不建議使用2。
捌、 PEN 和 CEPH 相關的嚴重皮膚過敏反應
SCARs (severe cutaneous adverse reactions) 乃是相當罕見之嚴重皮膚副作用,其中包括史帝芬強生症候群 (Stevens-Johnson syndrome,簡稱 SJS)、毒性表皮壞死溶解症 (toxic epidermal necrolysis,簡稱 TEN)、伴隨嗜伊紅性白血球增加與全身症狀的藥物反應 (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms,簡稱 DRESS)、急性廣泛性發疹性膿皰症 (acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis,簡稱 AGEP),以上皆屬於延遲型過敏反應。其中 SJS、TEN 的致死率為10-40%12。研究發現,PEN 和 CEPH 是引起 SJS、TEN、AGEP 最常見的抗生素,而 vancomycin 是引起 DRESS 最常見的抗生素13。若病人之前使用 PEN 或 CEPH 導致 SCARs,雖然這些病人大部份其後可安全地改用其他不同分類的抗生素 quinolones、glycopeptides、carbapenems,但是資料顯示仍然有一些病人可以耐受再次使用不同側鏈結構的 PEN 或 CEPH13。
玖、結論
證據顯示真正令人擔心之 PEN 經由 IgE 媒介的過敏反應並不常見,而 CEPH 過敏比 PEN 更為少見。現況使用稀釋的 penicillin G 來進行 PST,其結果只能作為參考,不可盡信。由於 PEN 或 CEPH 分子結構中造成過敏的主因是來自側鏈而非 β-lactam 環,因此 PEN 或 CEPH 過敏者,並不是絕對不能再次使用 PEN 或 CEPH,若有需要仍可謹慎使用不同側鏈的 PEN 或 CEPH。
Analysis of β-lactam Antibiotics Allergy
Chi-Yuan Cheng, Yi-Cheng Chen, Chi-Hua Chen
Department of Pharmacy, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Linkou
Abstract
The incidence of anaphylaxis to penicillins and cephalosporins is very rare. Allergy to penicillins and cephalosporins is caused mainly by reactions to the side chains of the molecules and less commonly to the β-lactam ring. Up to 90% of penicillin allergy individuals are able to tolerate penicillins, because majority of these patients don't have a true penicillin allergy, namely IgE-mediated reactions. Penicillin skin test (PST) is the most reliable method for evaluating IgE-mediated penicillin allergy; however, the result of diluted penicillin G solution as a reagent for PST is questionable. The overall cross allergy between penicillins and cephalosporins in individuals who report a penicillin allergy is approximately 1% and up to 2.55% in those with a confirmed penicillin allergy. For penicillin-allergic patients, the use of third- or fourth-generation cephalosporins or cephalosporins with dissimilar side chains than the offending penicillin carriers a negligible risk of cross allergy. Patients with a history of penicillin or cephalosporin allergy could administer penicillins or cephalosporins with dissimilar side chains with caution if necessary.
參考資料:
1.Kerr JR. Penicillin allergy: a study of incidence as reported by patients. Br J Clin Pract 1994;48:5-7.
2. Joint Task Force on Practice Parameters; American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology; American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology; Joint Council of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. Drug allergy: an updated practice parameter. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2010;105:259-73.
3. Kemp SF. Pathophysiology of anaphylaxis. UpToDate [updated 2015 Jun 09]
4. Pichichero ME, Zagursky R. Penicillin and cephalosporin allergy. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2014;112:404-12.
5. Sogn DD, Evans R, Shepherd GM, et al: Results of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases collaborative clinical trial to test the predictive value of skin testing with major and minor penicillin derivatives in hospitalized adults. Arch Intern Med 1992;152:1025-32.
6. Gadde J, Spence M, Wheeler B, et al: Clinical experience with penicillin skin testing in a large inner-city STD clinic. JAMA. 1993;270:2456-63.
7. Pichichero ME. Cephalosporins can be prescribed safely for penicillin-allergic patients. J Fam Pract 2006;55:106-12.
8. Romano A. Cephalosporin allergy: Clinical manifestations and diagnosis. UpToDate [updated 2014 Jun 17]
9. Herbert ME, Brewster GS, Lanctot-Herbert M. Medical myth: ten percent of patients who are allergic to penicillin will have serious reactions if exposed to cephalosporins. West J Med 2000;172:341.
10. Campagna JD, Bond MC, Schabelman E, et al: The use of cephalosporins in penicillin-allergic patients: a literature review. J Emerg Med 2012;42:612-20.
11. Sastre J, Quijano LD, Novalbos A, et al: Clinical cross-reactivity between amoxicillin and cephadroxil in patients allergic to amoxicillin and with good tolerance of penicillin. Allergy 1996;51:383-6.
12. Chan HL, Stern RS, Arndt KA, et al: The incidence of erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis. A population-based study with particular reference to reactions caused by drugs among outpatients. Arch Dermatol 1990;126:43-7.
13. Lin YF, Yang CH, Sindy H, et al: Severe cutaneous adverse reactions related to systemic antibiotics. Clin Infect Dis 2014;58:1377-85.

