摘要
目前治療幽門螺旋桿菌首選治療方法仍為質子幫浦阻斷劑 (Proton-pump inhibitors)、clarithromycin 和 amoxicillin (或 metronidazole) 所組成之標準三合一療法。但近年來,隨著抗藥菌株的增加,幽門螺旋桿菌的滅菌成功率有下降之趨勢,因此有許多新的療法被發展出來。目前,大部份治療準則仍是三合一療法為首選。但此一療法在全球許多地區的失敗率高達20%以上。系列性治療是另一種第一線治療方法,其滅菌成功率約84.3%,而高劑量 PPI 和 amoxicillin 組成之二合一療法不論在第一線或第二線治療都有相當優異的表現,可能為將來在幽門螺旋桿菌的治療上另一個新的選擇。在第二線治療上,以 PPI、鉍劑、tetracycline 和 metronidazole 所組成之四合一療法或以 PPI、amoxicillin 和 levofloxacin 組成之三合一療法作第二線治療處方為主。
關鍵字: 幽門螺旋桿菌、Helicobacter pylori、Triple therapy、Sequential therapy、Quadruple therapy、High-dose dual therapy
壹、前言
幽門螺旋桿菌 (Helicobacter pylori) 是螺旋狀具有纖毛的細菌,2005諾貝爾獎得主 Marshall 及 Warren 於1983年發現。在感染幽門桿菌之後,胃會慢性發炎。往往是引起胃潰瘍與胃癌的主要原因,唯有成功根除幽門螺旋桿菌才可預防上述疾病的發生1。但為了面對抗生素耐藥性的問題日益嚴重2,加上病人對藥物之順從性不佳,標準三合一療法的失敗率逐漸上升。於是除了傳統的第一線療法 (三合一療法) 外,其它各類療法分別被提出 (如系列性治療法、高劑量二合一療法、四合一療法以及其他類等)。期盼新的治療組合可以達到根除幽門螺旋桿菌的效果。
貳、治療 (表一)
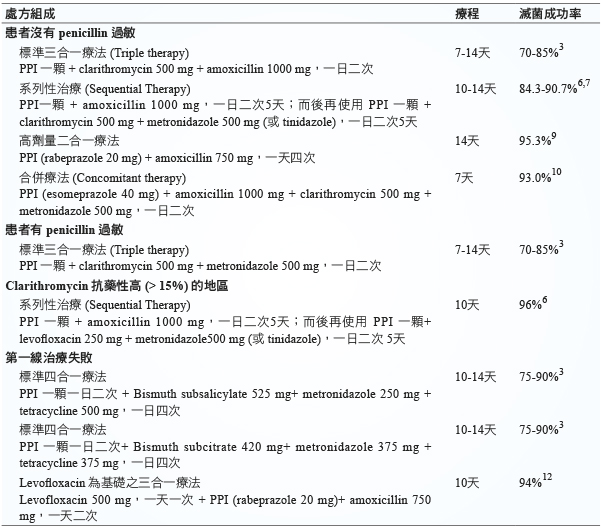
一、標準三合一療法 (Triple therapy)
目前幽門螺旋桿菌第一線治療方法在 clarithromycin 抗藥性少 (< 15%) 的地區,仍為由質子幫浦抑制劑 (proton pump inhibitor, PPI)、clarithromycin 和 amoxicillin (如果對 penicillin 過敏的患者可改用 metronidazole) 所組成之標準三合一療法3。PPI 可使用 lansoprazole 30 mg、omeprazole 20 mg、pantoprazole 40 mg、rabeprazole 20 mg 或 esomeprazole 40 mg;Clarithromycin 之劑量為一次500 mg;amoxicillin 為一次1000 mg (或 metronidazole 500 mg),每日口服二次,療程為10至14天。
基本上 PPI、clarithromycin 加上 amoxicillin 與 PPI、clarithromycin 加上 metronidazole 療效是相當的。而治療的療程以7天為主滅菌成功率約72.9%,而14天療程為81.9%的滅菌成功率 (RR 0.66 95% CI 0.60-0.74; NNT 11, 95% CI 9- 14 )。而不良反應發生率7天療程15.5%,而14天療程為19.4% (RR 1.21, 95% CI 1.06 -1.37; NNTH 31, 95% CI 18- 104)4。不過患者服用後往往出現因為服藥的顆粒數太多或藥物之副作用自行擅自停藥的情形。(常見藥物之副作用見表二)5
表一 幽門螺旋桿菌的治療3,6,7,9,10,12
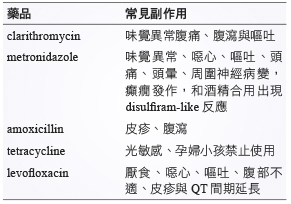
表二 幽門螺旋桿菌治療藥品常見副作用 (最常見副作用是由於 clarithromycin 與metronidazole 產生味覺異常 (金屬味))5。
二、系列性治療 (Sequential Therapy)
系列性治療係由義大利學者 Zullo 所提出,是先給病人一天兩次的 PPI 和 amoxicillin 5天,而後再給5天 PPI、clarithromycin 和 metronidazole (或 tinidazole)。在 penicillin 過敏患者或 clarithromycin 抗藥性高 (> 15%) 的地區可改用 levofloxacin (250 mg 一天兩次)6。
系列性治療滅菌成功率84.3% (95% CI 82.1%-86.4%) 比標準三合一療法更有效地根除幽門螺旋桿菌 (RR 1.21, 95% CI 1.17-1.25; NNT 6 , 95% CI 5%-7%)7。
而在台灣一多中心隨機試驗 (a multicentre, randomised trial),14天系列性治療 (前七天 lansoprazole 30 mg、amoxicillin 1 g,隨後七天 lansoprazole 30 mg、clarithromycin 500 mg 和 metronidazole 500 mg 一天兩次) 比上14天標準三合一療法。14天系列性治療滅菌成功率可高達90·7% (95% CI 87·4-94·0) 而14天標準三合一療法滅菌成功率82·3% (95% CI78·0-86·6),而不良反應兩者無差異8。
而含 levofloxacin 系列性治療,藥品費用比起含 clarithromycin 或 amoxicillin 較高,但有更高滅菌成功率 (96 vs 81%),更有效地根除幽門螺旋桿菌。
三、高劑量二合一療法 (High-dose Dual Therapy)
由於 amoxicillin 抗藥性較低,加上提高胃中 pH 值,可有效增加 amoxicillin 的藥效。於是使用高劑量 PPI 與 amoxicillin 二合一療法,治療幽門螺旋桿菌,處方包括 rabeprazole 20 mg 加上 amoxicillin 750 mg,一天四次使用14天。高劑量二合一療法可達到95.3%滅菌成功率 (95% CI, 91.9-98.8%),比起10天系列性治療85.3% (95% CI, 79.6-91.1%) 和5天標準三合一療法80.7% (95% CI, 74.3-87.1%) 都要高出許多。而安全性並無差異出現。
高劑量二合一療法亦可用於之前曾治療過的患者,仍然保有89.3%滅菌成功率 (95% CI, 80.9-97.6%),比起10天系列性治療51.8% (95% CI, 38.3-65.3%) 和7天含 levofloxacin 三合一療法78.6% (95% CI,67.5-89.7%) 效果都更好9。
四、合併療法 (Concomitant therapy)
以 PPI (esomeprazole)、amoxicillin、clarithromycin 和 metronidazole 組成的7天合併療法 (93.0%; 95% CI: 88.3%-97.7%),與10天系列性治療 (92.3%; 95% CI 87.5%-97.1%)(p = 0.83) 滅菌成功率相似,且病人之藥物順從性好且使用上也較系列性治療方便10。
五、標準四合一療法 (Quadruple therapy)
在 clarithromycin 產生抗藥性 (> 15%)的地區,或者第一線治療失敗,可建議使用含鉍之四合一療法。組成為 PPI、鉍劑 (如 bismuth subcitrate 或 bismuth subsalicylate)、tetracycline 和 metronidazole,療程為10至14天。此一治療方法滅菌成功率不一,從75%到90%不等3。
六、以 levofloxacin 為基礎之三合一療法
在第二線治療時幽門螺旋桿菌對 metronidazole 之抗藥比率高達51%,但對 amoxicillin 及 levofloxacin 的抗藥比率僅2%及15%11。以 PPI、amoxicillin 和 levofloxacin 組成之三合一療法,針對 metronidazole 之抗藥性菌有顯著療效。在第二線滅菌治療的成功率與標準的四合一療法相當而且副作用較少12。
參、總結
幽門螺旋桿菌治療其成功率常受各地區抗藥性比率高低所影響。就處方的選擇應該就藥效、價格與不良反應是否發生做整體的評估,以給予患者適當之滅菌治療,並避免其消化性潰瘍之復發及幽門螺旋桿菌抗藥菌株的產生。
Tratment of Helicobacter Pylori Infection
Zheng-Ren Lin1, Chien-Ying Lee2
Department of Pharmacy, Chung Shan Medical University Hospital1
Department of Pharmacology, Chung Shan Medical University2
Abstract
Currently, the first-line therapy for Helicobacter pylori infection is standard triple therapy, consisting of a proton pump inhibitor, clarithromycin and amoxicillin. But in recent years, with the increase in drug- resistant strains of Helicobacter pylori sterilization success rate has declined the trend, so there are many new treatments being developed. Currently, most treatment guidelines triple therapy is still the first choice for Helicobacter pylori infection, but this treatment failure rates in many parts of the world up to 20%. Series of first-line therapy is another method of treatment, sterilization succes rate of 84.3%, while high-dose dual therapy and concomitant therapy have been developed and achieve a high eradication rate. The second-line therapy, most guidelines suggest a quadruple therapy. Recently, a triple therapy with the combination of a PPI, levofloxacin and amoxicillin and also achieve a high eradication rate.
參考資料:
1. Medeiros JA, Pereira MI: The use of probiotics in Helicobacterpylori eradication therapy. J Clin Gastroenterol 2013; 47: 1-5.
2. Huang AH, Sheu BS, Yang HB, et al: Impact of Helicobacterpylori antimicrobial resistance on the outcome of 1-week lansoprazole-based triple therapy. J Formos Med Assoc2000; 99: 704-9.
3. Chey WD, Wong BCY: American College of Gastroenterology Guideline on the Management of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Am J Gastroenterol 2007; 102:1808.
4. Yuan Y, Ford AC, Khan KJ, et al: Optimum duration of regimens for Helicobacter pylori eradication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;12:CD008337.
5. Crowe SE: Treatment regimens for Helicobacter pylori. UpToDate online. Available at http://www.uptodate.com. (cited:12/14/2015)
7. Gatta L, Vakil N, Vaira D, et al: Global eradication ratesfor Helicobacter pylori infection: systematic review and meta-analysis of sequential therapy. BMJ 2013; 347: f4587
8. Liou JM, Chen CC, Chen MJ, et al: Sequential versus triple therapy for the first-line treatment of Helicobacter pylori: a multicentre, open-label, randomised trial.Lancet 2013; 381: 205-213
9. Yang JC, Lin CJ, Wang HL, et al: High-dosedual therapy is superior to standard first-line or rescue therapy for Helicobacter pylori infection. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015; 13:895-905.e5
10. Wu DC, Hsu PI, Wu JY, et al: Sequential and concomitanttherapy with four drugs is equally effective for eradicationof H. pylori infection. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2010; 8:36-41.
11. Wu DC, Hsu PI, Chen A, et al: Randomized comparison oftwo rescue therapies for Helicobacter pylori infection. Eur JClin Invest 2006; 36: 803-9.
12. Nista EC, Candelli M, Cremonini F, et al: Levofloxacin based triple therapy vs. quadruple therapy in second-line Helicobacter pylori treatment: a randomized trial. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003; 18: 627-33.

