摘要
在臺灣陸續核准 empagliflozin、dapagliflozin 二個「鈉-葡萄糖共同轉運蛋白2」抑制劑 (sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor,SGLT2i),而 canagliflozin 在台尚無上市。SGLT2i 適應症為治療第二型糖尿病的二線藥物。衛福部於2015年6月及12月兩次發布使用 SGLT2i 可能導致糖尿病酮酸中毒 (diabetic ketoacidosis,DKA) 之安全性資訊。不同於典型 DKA,SGLT2i 發生 DKA 時可能血糖正常或僅些微升高,因此臨床上可能會被忽略,造成未及時發現而導致延遲治療。容易引發 DKA 的因素包括喝水量不夠、將接受手術、進食減少、大量飲酒。雖然第二型糖尿病患者使用 SGLT2i 引起 DKA 十分少見,但是由於 SGLT2i 使用已日益頻繁再加上 DKA 具有生命威脅需要立即治療,因此在使用 SGLT2i 期間應密切注意任何 DKA 相關症狀 (腹痛、噁心/嘔吐、疲憊、意識改變、呼吸急促或過度換氣)。醫療人員應衛教病人避免從事容易引發 DKA 的誘發因子,若無法避免則要暫停 SGLT2i 甚至考慮永久不用此類藥品,以確保病人安全。
關鍵字: 鈉-葡萄糖共同轉運蛋白2抑制劑、糖尿病酮酸中毒、sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor、diabetic ketoacidosis
壹、前言
在臺灣陸續核准 empagliflozin、dapagliflozin 二個「鈉-葡萄糖共同轉運蛋白2」抑制劑 (sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor,以下簡稱 SGLT2i),而 canagliflozin 在台尚無上市。SGLT2i 可抑制葡萄糖經由近端腎小管再吸收而達到降低血糖,適應症為治療第二型糖尿病的二線藥物。除此之外,它們也能降低體重、血壓、心血管事件1,因此其使用量日增。然而,衛福部於104年6月及12月兩次發布使用 SGLT2i 可能導致糖尿病酮酸中毒 (diabetic ketoacidosis,簡稱 DKA) 之安全性資訊2,本文將就此議題作探討。
貳、DKA 發生率
DKA 最常見於第一型糖尿病病人,發生率為0.46-0.80%3。第二型糖尿病人者使用 SGLT2i 罕見引起 DKA。最近一個統合分析發現 SGLT2i 引起 DKA 的機會是0.1%與對照組0.06%之間無差異 (危險比1.71, 95%信賴區間0.56-5.20)4。
參、血糖值正常的 DKA
不同於典型 DKA 發生時血糖 > 250 mg/dL 甚至更高,SGLT2i 發生 DKA 時可能血糖正常 < 200 mg/dL (euglycemic DKA,以下簡稱 euDKA) 或僅些微升高。發生 euDKA 的可能原因有最近開始使用胰島素、大量喝酒、碳水化合物攝取量偏低、慢性肝病、懷孕5。和典型 DKA 一樣,euDKA 也是有生命威脅屬於醫療緊急事件需要立刻治療,但由於 euDKA 發生時血糖並不高,臨床上可能會被忽略,造成未及時發現而導致延遲治療。
肆、機轉
SGLT2i 引起 DKA 的可能機轉有二6,7:一、由於它降低血糖使得胰島素製造下降,當血液中胰島素濃度明顯不足時會導致脂肪開始分解產生游離脂防酸 (free fatty acid,FFA),而 FFA 增加會造成肝臟肝醣合成增加以及酮體 (ketone body) 生成;二、SGLT2i 本身就會直接促進肝臟肝醣合成以及酮體生成。
伍、診斷及臨床症狀
診斷 DKA 在抽血檢查方面除了血糖外,還必須符合兩個條件8:一、酮體生成:血中出現酮體。由於 DKA 產生的酮體主要是 β-hydroxybutyrate,所以檢驗尿液並不準,因為尿中只能測到酮體的另一成份 acetoacetate;二、出現代謝性酸中毒:動脈血 pH < 7.3和碳酸氫鹽 (bicarbonate) < 15 mmol/L,以及陰離子間隙 (anion gap) > 12 mmol/L。DKA 的臨床症狀常見腹痛、噁心/嘔吐、疲憊,此外也可能出現意識改變、呼吸急促或過度換氣8。
陸、誘發 DKA 的相關風險因素
從一些使用 SGLT2i 引起 DKA 的通報案例中發現容易引發 DKA 的因素包括:減少胰島素劑量或停止胰島素注射、感染之急性發熱性疾病、脫水、因疾病或手術而減少熱量攝取、胰臟疾病而有胰島素分泌不足之虞 (如第一型糖尿病及胰臟炎或胰臟手術病史) 和酗酒2。此外,也發現原本診斷為第二型糖尿病病人使用 SGLT2i 發生 DKA 者,其中有36%後來診斷改為成人隱匿性自身免疫糖尿病 (latent autoimmune diabetes of adulthood,LADA)7。LADA 原本是第一型糖尿病,但常常被誤診為第二型糖尿病。由於 LADA 隨著病情發展,胰島素分泌快速下降,再加上 SGLT2i 使得血液中胰島素濃度明顯不足,如此將會提高發生 DKA 的機會。因此對於糖尿病發病年齡 < 50歲、發病一開始就出現多食/多尿/劇渴/消瘦之明顯症狀者要先確定是否為 LADA 病人9,若診斷為 LADA 應避免使用 SGLT2i。
柒、預防 DKA 發生的建議
對於已正在接受胰島素治療的第二型糖尿病患者,這群病人是發生 DKA 的高危險族群,若要加入 SGLT2i 需要告知病人不可自行停掉胰島素或降低其劑量10。衛教病人有關 DKA 的臨床症狀,一旦出現症狀應立刻停用 SGLT2i 並立即就醫,醫療人員應警覺 DKA 的發生,即使當時病人的血糖值正常,也應建議病人抽血檢測酮體10。對於尚未接受胰島素治療的第二型糖尿病患者,加入 SGLT2i 也要注意 DKA 的發生,尤其是長期第二型糖尿病患者可能體內胰島素已缺乏,若再合併上述 DKA 的誘發因子情況下仍然有可能引發 DKA10。
由於 SGLT2i 有利尿作用,使得病人處在脫水的風險中,而脫水本身就會誘發 DKA 的發生;因此醫療人員必須告知使用 SGLT2i 的病人每天絕對要喝足夠的水10。若是患者無法多喝水,應避免使用 SGLT2i。此外,使用 SGLT2i 期間不要刻意減少碳水化合物的攝取10。
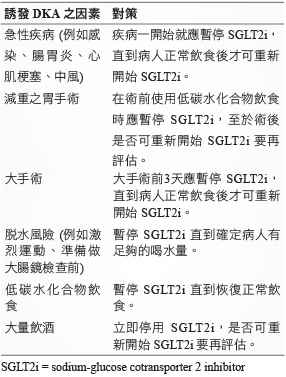
表一列出在面對潛在誘發 DKA 之因素下,使用 SGLT2i 的相應對策。由於 SGLT2i 的半衰期範圍為11-13小時,停用 SGLT2i 後其藥效仍會持續一段時間,為確保停藥後它們在體內幾乎沒有殘留藥量,因此建議在大手術前3天 (約5個半衰期) 就應暫停 SGLT2i,如此可預防 DKA 的發生10。
表一 使用 SGLT2抑制劑之預防 DKA 發生的對策10
捌、結論
雖然第二型糖尿病患者使用 SGLT2i 引起 DKA 十分少見,但是由於 SGLT2i 使用已日益頻繁再加上 DKA 具有生命威脅需要立即治療,因此在使用 SGLT2i 期間應密切注意任何 DKA 相關症狀,患者可能在血糖值正常的情形下也會發生 DKA。醫療人員應衛教病人避免從事容易引發 DKA 的誘發因子,例如喝水量不夠、將接受手術、進食減少、大量飲酒,若無法避免則要暫停 SGLT2i 甚至考慮永久不用此類藥品,以確保病人安全。
Diabetic Ketoacidosis Induced by SGLT2 Inhibitors: Clinical Review
Chi-Yuan Cheng, Tzu-Cheng Tsai
Department of Pharmacy, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Linkou
Abstract
In Taiwan, two sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i), namely empagliflozin and dapagliflozin were approved and canagliflozin was not listed. SGLT2i is indicated for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) as the second-line therapy. In 2015 June and December, Taiwan Ministry of Health and Welfare announced that SGLT2i use may lead to diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). SGLT2i induced DKA is different from typical DKA shown as relatively high blood sugar, the former is with normal blood sugar or slightly higher, and hence might be ignored resulting in delayed treatment. Precipitating factors of DKA includes water deficiency, surgery, decreased food intake, and heavy alcohol consumption. The incidence of SGLT2i-associated DKA in type 2 DM is rare; however, frequencies of prescribing SGLT2i much increased plus DKA remains a medical emergency needed to be treated in a quick manner, any SGLT2i-treated patient with symptoms of DKA (abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, altered mental status, shortness of breath or hyperventilation) should to be closely monitored. Medical personnel should educate patients to avoid DKA-related precipitating factors. Suspend SGLT2i temporarily if those factors cannot be avoided, and even consider to stop SGLT2i permanently to ensure patient safety.
參考資料:
1.Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, et al: Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2015;373:2117-28.
2. http://www.fda.gov.tw/TC/siteList.aspx?sid=1571
3. Kitabchi AE, Umpierrez GE, Murphy MB, et al: Hyperglycemic crises in adult patients with diabetes: a consensus statement from the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2006;29:2739-48.
4. Tang H, Li D, Wang T, et al: Effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on diabetic ketoacidosis among patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Care 2016;39:e123-4.
5. Modi A, Agrawai A, Morgan F: Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis. Curr Diabetes Rev 2016 Apr 21. [Epub ahead of print]
6. Ogawa W, Sakaguchi K: Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis induced by SGLT2 inhibitors: possible mechanism and contributing factors. J Diabetes Investig 2016;7:135-8.
7. Burke KR, Schumacher CA, and Harpe SE: SGLT2 Inhibitors: a systematic review of diabetic ketoacidosis and related risk factors in the primary literature. harmacotherapy 2017;37:187-94.
8. Chiasson JL, Aris-Jilwan N, Belanger R, et al: Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis and the hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state. CMAJ 2003;168:859-66.
9. Fourlanos S, Perry C, Stein MS, et al: A clinical screening tool identifies autoimmune diabetes in adults. Diabetes Care 2006;29:970-5.
10. Goldenberg RM, Berard LD, Cheng AY, et al: SGLT2 inhibitor–associated diabetic ketoacidosis: clinical review and recommendations for prevention and diagnosis. Clin Ther 2016;38:2654-64.
通訊作者:鄭吉元/通訊地址:桃園市龜山區復興街5號
服務單位:林口長庚紀念醫院藥劑部藥師/聯絡電話:(O) 03-3281200 ext 2915

