胰管腺癌之異常基因及其精準醫療
鄭吉元1、陳宜正1、蔡慈貞2、張文震3
1林口長庚紀念醫院藥劑部藥師
2林口長庚紀念醫院藥劑部藥師、2新生醫護管理專科學校兼任講師、
3林口長庚紀念醫院腫瘤科醫師
摘要
胰管腺癌 (pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma,PDAC) 是胰臟癌中最常見的型態,佔胰臟癌的90%。PDAC的預後差,1年存活率不到20%。現階段治療晚期PDAC的策略仍是以化療藥物為主,針對微衛星不穩定 (microsatellite instability,MSI) 的PDAC病人,可後線使用免疫檢查點抑制劑pembrolizumab。近年來,因次世代基因定序 (next generation sequencing,NGS) 技術的應用,增進我們對PDAC異常基因的瞭解。KRAS、CDKN2A、TP53、SMAD4這4個基因突變是PDAC主要的異常基因,其中以KRAS突變的發生率最高,可超過90%。有高達24%之PDAC患者會出現DNA受損修復 (DNA damage repair,DDR) 基因突變,例如BRCA1、BRCA2突變會造成DDR產生缺陷,此時可第一線給予鉑類化療藥(如:cislpatin)或是PARP抑制劑(如:olaparib)。美國和臺灣FDA皆已核准olaparib單一療法之維持治療,可用於遺傳性BRCA突變且經第一線含鉑化療至少16週後疾病未惡化之轉移性胰腺癌病人。此外,針對染色質重塑 (chromatin remodeling) 相關基因突變,可使用DNA甲基轉移酶抑制劑decitabine和azacitidine以及組織蛋白脫乙醯酶抑制劑vorinostat等,這些藥物皆在進行臨床試驗。
關鍵字: 胰管腺癌、精準醫療、pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma、precision medicine
壹、前言
胰管腺癌 (pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma,以下簡稱PDAC) 是胰臟癌中最常見的型態,佔胰臟癌的90%1。PDAC的預後差,1年存活率不到20%,5年存活率為5-7%1,主要原因是大部份PDAC病人在診斷當下已是晚期或轉移性疾病。目前治療晚期PDAC的策略是以化療藥物為主,包括單獨使用gemcitabine、gemcitabine併用nab-paclitaxel、FOLFIRINOX組合 (fluorouracil / leucovorin / irinotecan / oxaliplatin)、TS-1單用、TS-1併用gemcitabine等,但治療效果有限,中位存活期不到1年2。針對「DNA錯誤配對修復機制有缺陷 (mismatch repair deficiency, dMMR)」或稱為「微衛星不穩定(microsatellite instability, MSI) 」的PDAC病人,可後線使用免疫檢查點抑制劑pembrolizumab2。因此,PDAC的治療十分需要新的藥物。
近年來,因次世代基因定序 (next generation sequencing,NGS) 技術的應用,增進我們對癌症分子生物學及其異常基因的瞭解,也開啟了針對異常基因之標靶藥物的研發。NGS又稱為大量平行定序 (massively parallel sequencing),乃是利用超音波或酵素裁切等方式將DNA打斷成200-500 bp的片段大小,接著將其末端接上轉接子 (adaptor),藉由轉接子會與晶片上的互補序列相結合,再以鏈終止法 (chain-termination method) 同時間大量進行DNA定序,將定序後的大量資訊與現有的資料庫進行比對分析以定出基因序列。隨著NGS的問世,大幅縮短了基因定序時間「精準醫療」乃是利用個人基因型或是基因表現及臨床資訊,選擇最適合個人使用之藥物治療或預防方式,以期達到藥品最大療效與最小的副作用。本文將探討PDAC的異常基因,以及PDAC的精準醫療。
貳、胰管腺癌的異常基因
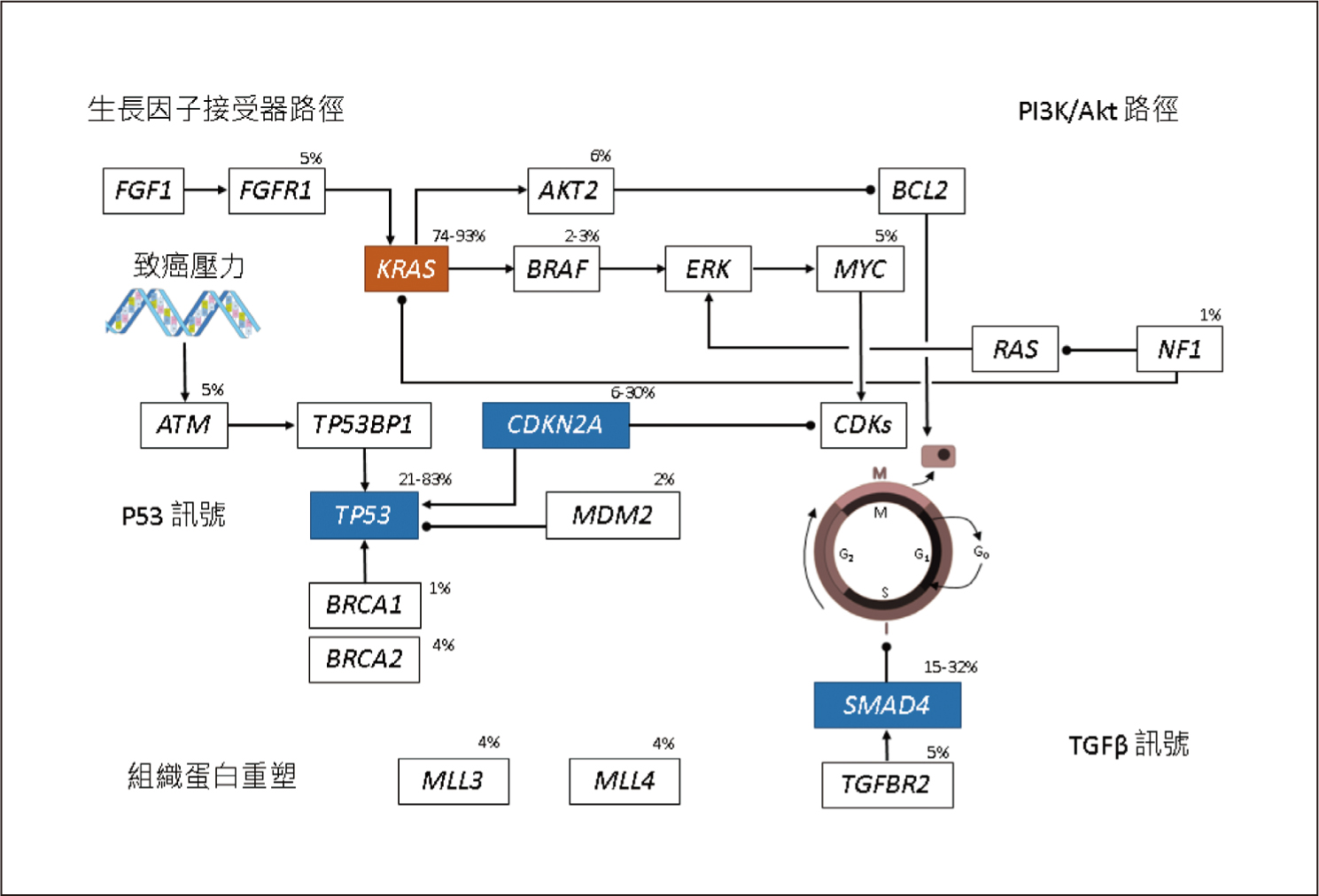
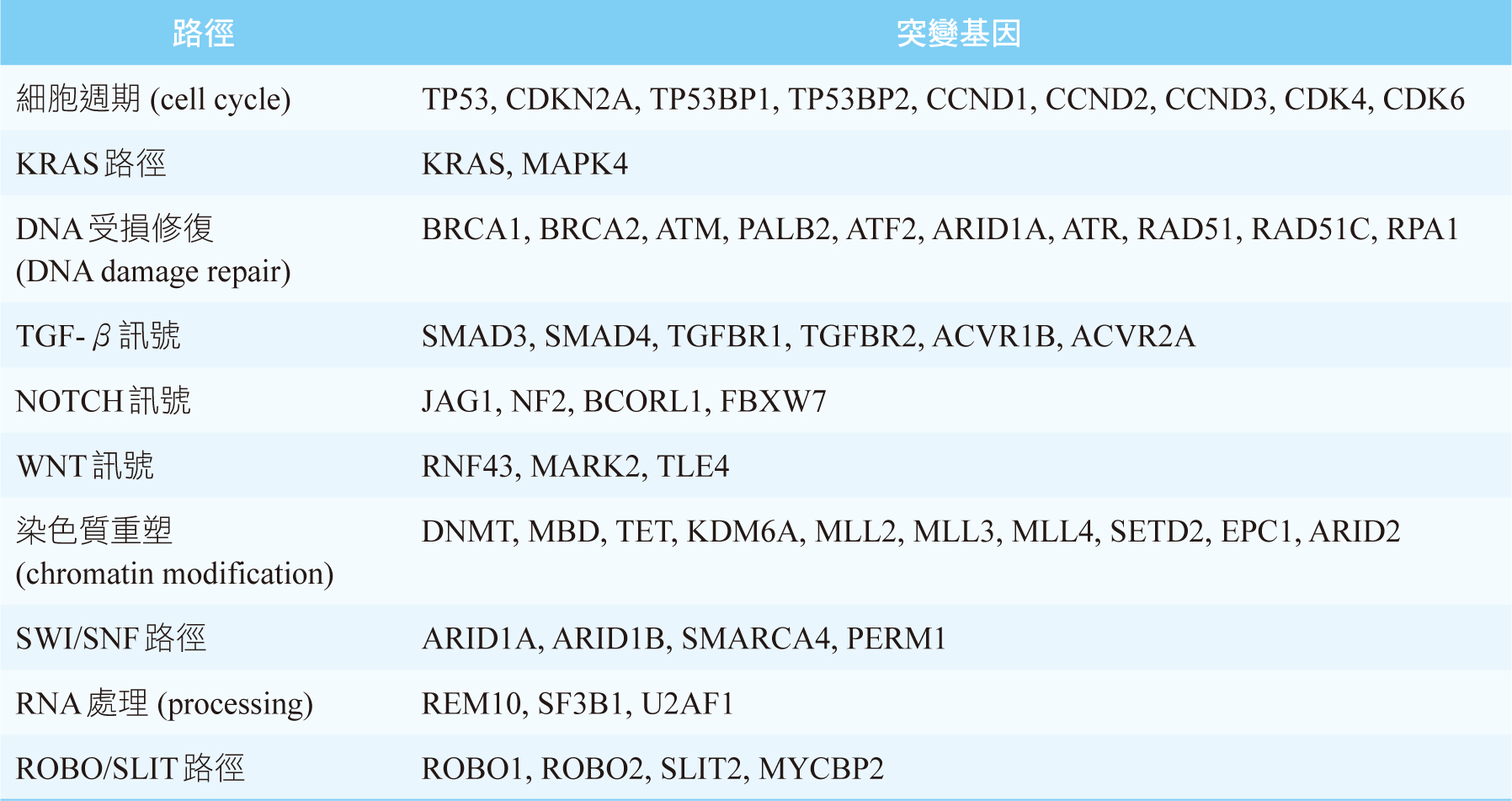
KRAS、CDKN2A、TP53、SMAD4這4個基因突變是PDAC主要的異常基因,其中以KRAS突變的發生率最高,可超過90%4,見圖一。基因縮寫的全名見文末。PDAC的發生非常依賴KRAS突變,所以PDAC是一個對KRAS上癮 (KRAS-addicted) 的癌症4。TP53、CDKN2A這2個腫瘤抑制基因和細胞週期 (cell cycle) 有關,見表一5。SMAD4則和乙型轉化生長因子 (transforming growth factor beta, TGF-β) 訊號有關,見表一5。胰管腺癌的主導基因 (driver gene) 除了上述的4個基因外,還有RNF43 (WNT訊號), ARID1A (DNA受損修復、SWI/SNF路徑), TGFBR2 (TGF-β訊號)4,5。RNF43為腫瘤抑制基因,一旦突變會使其喪失原本抑制腫瘤的功能5。
圖一 胰管腺癌常見的異常基因4 (百分比表示該基因突變的發生率;基因縮寫的全名見文末)
表一 胰管腺癌的突變基因及其相關的路徑5,6 (基因縮寫的全名見文末)
有高達24%之PDAC患者會出現DNA受損修復 (DNA damage repair,DDR) 基因突變5,例如BRCA1、BRCA2突變會造成DDR產生缺陷。BRAF V600E突變存在於3%的PDAC病人,這群患者絕對不會出現KRAS突變5。
近年來發現PDAC的發生除了和基因有關,也和染色質 (chromatin) 相關6。染色質就是DNA加上周圍環繞的蛋白質和RNA6。染色質重塑 (chromatin modification) 是一種超越基因的機制,乃是利用修飾染色質方式來控制基因的活性,其中將DNA甲基化 (DNA methylation),即表觀基因組學 (epigenomics)染色質重塑的典型手法6,7。此外,組織蛋白重塑 (histone modification) 也會影響染色質重塑4。PDAC患者可能會被檢測出與染色質重塑相關基因的突變,見表一。其中DNMT, MBD, TET是屬於DNA甲基化相關的基因6,MLL基因則和組織蛋白重塑相關4。
參、胰管腺癌之精準醫療
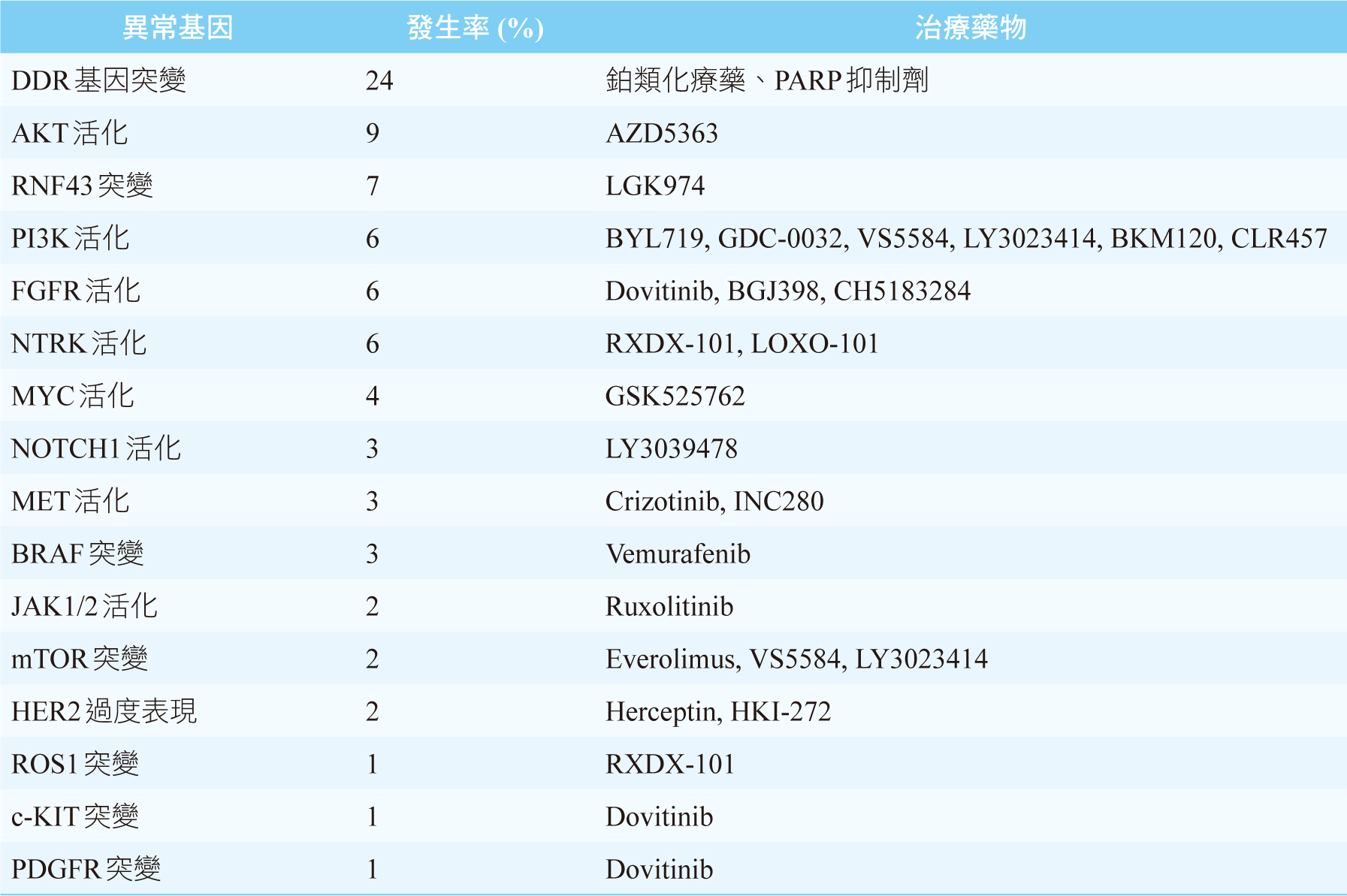
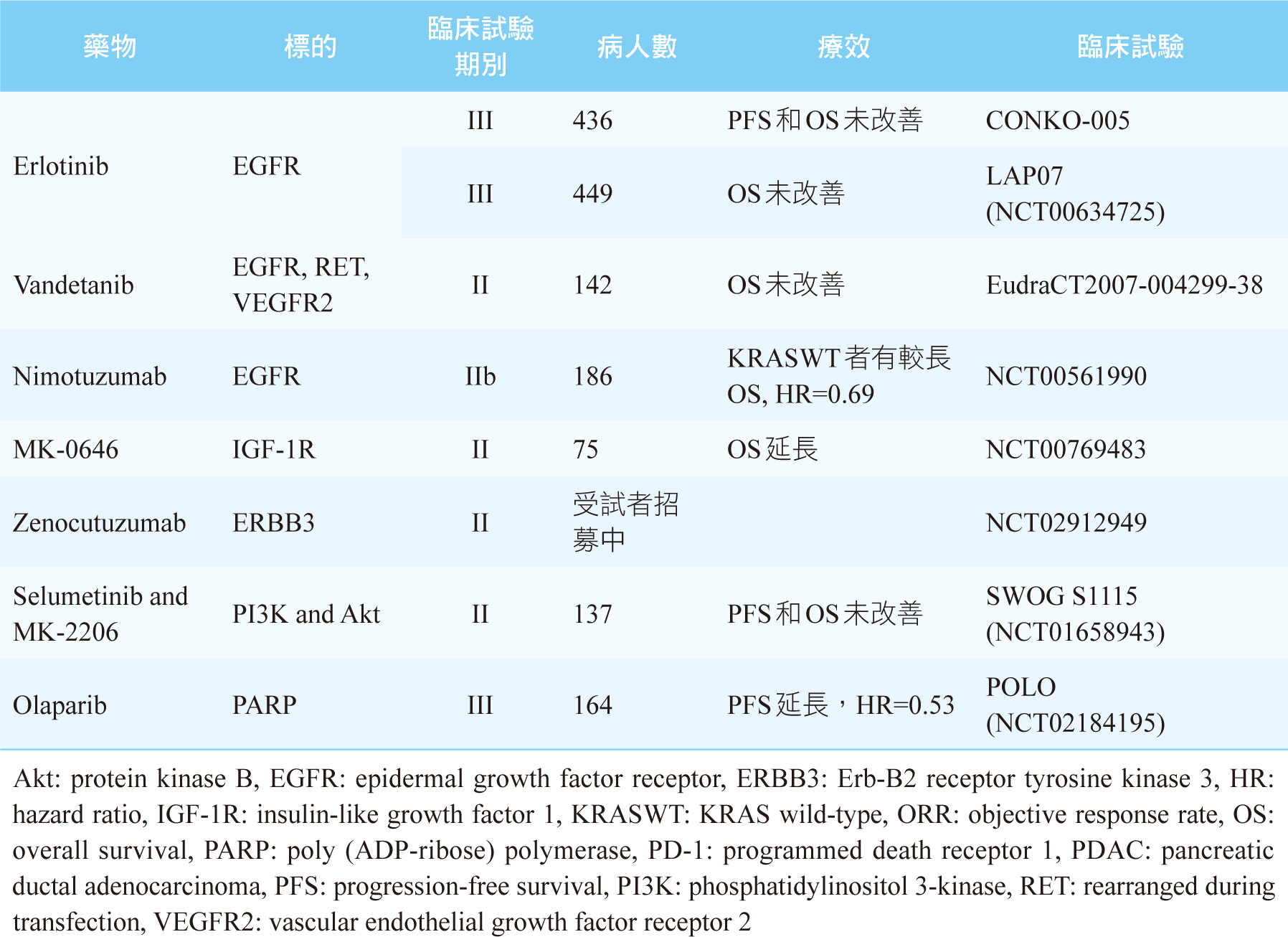
雖然我們知道KRAS、CDKN2A、TP53、SMAD4這4個基因突變是PDAC主要的異常基因,但是現階段尚未有相對應的標靶藥物上市可以使用。目前針對PDAC異常基因可行的治療藥物,絕大部份都是針對發生率偏低的異常基因,見表二,其治療效果仍不明確。唯一例外的是有高達24%之PDAC患者會出現DDR基因突變5,例如BRCA1、BRCA2突變,此時可第一線給予鉑類化療藥(如:cisplatin)或是PARP (poly ADP- ribose polymerase) 抑制劑(如:olaparib)2,5。美國和臺灣FDA皆已核准olaparib單一療法之維持治療,可用於遺傳性BRCA突變且經第一線含鉑化療至少16週後疾病未惡化之轉移性胰腺癌病人。此核准乃是根據第三期POLO研究 (NCT02184195) 結果,使用olaparib維持治療之無疾病惡化存活期 (progression-free survival,PFS) 約是安慰劑組的兩倍 [PFS: olaparib 7.4個月;安慰劑組3.8個月 (HR 0.53, p=0.004)] 8。表三是整理至今標靶藥物用於PDAC之主要和樞紐臨床試驗及其療效9。
表二 治療胰管腺癌可行的治療藥物5
表三 最新的有關於標靶藥物用於PDAC之主要和樞紐臨床試驗及其療效9
此外,還有多項與PDAC精準醫療相關之臨床試驗正在進行中,包括針對細胞週期路徑相關的基因異常使用CDK4/6抑制劑palbociclib (NCT03065062)2,以及針對染色質重塑相關基因突變使用DNA甲基轉移酶 (DNA methyltransferase) 抑制劑decitabine (NCT02685228) 和azacitidine (NCT01167816) 以及組織蛋白脫乙醯酶 (histone deacetylase) 抑制劑vorinostat (NCT00948688) 等皆在進行臨床試驗10。
肆、結論
儘管幾十年來努力於PDAC的治療,至今成果仍不理想。隨著人類基因的解碼,醫學已進入精準醫療時代。許多PDAC之精準醫療的臨床試驗正在進行中,我們急切地等待其結果。現階段治療晚期PDAC的策略仍是以化療藥物為主,針對MSI的PDAC病人,可後線使用免疫檢查點抑制劑pembrolizumab。PDAC患者若出現DDR基因突變,例如BRCA1、BRCA2突變,此時可第一線給予鉑類化療藥或是PARP抑制劑(如:olaparib)。未來希望藉由對PDAC基因表現有更多的瞭解、更多嶄新的標靶藥物研發以及依據不同的PDAC基因型進行更多的臨床試驗,使得PDAC之精準醫療可以更上一層樓。
基因縮寫的全名
ACVR1B: Activin receptor type 1B
AKT: Protein Kinase B
ARID1A: AT-rich interaction domain 1A
ATF2: Activating transcription factor 2
ATM: Ataxia telangiectasia mutated
ATR: Ataxia telangiectasia and rad3-related
protein
BCL2: B-cell lymphoma 2
BCORL1: BCL6 corepressor like 1
BRAF: v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene
homolog B1
BRCA1/2: Breast cancer gene 1/2
CCND1: Cyclin D1
CDK6: Cyclin-dependent kinase 6
CDKN2A: Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A
DNMT: DNA methyltransferase
EPC1: Enhancer of polycomb homolog 1
ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
FBXW7: F-box and WD repeat domain containing 7
FGF1: Fibroblast growth factor 1
FGFR1: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1
JAG1: Jagged-1
KDM6A: Lysine demethylase 6A
KRAS: Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog
MAPK4: Mitogen-activated protein kinase 4
MARK4: Microtubule affinity regulating kinase 4
MBD: Methyl-CpG binding domain
MDM2: Mouse double minute 2 homolog
MLL: Mixed-lineage leukemia
MYC: Myelocytomatosis
MYCBP2: MYC binding protein 2
NF1: Neurofibromatosis type 1
PALB2: Partner and localizer of BRCA2
PERM1: PPARGC1 and ESRR induced regulator,
muscle 1
RAS: Rat sarcoma
RNF43: Ring finger protein 43
ROBO2: Roundabout guidance receptor 2
RPA: Replication protein A
SETD2: SET domain-containing 2
SF3B1: Splicing factor 3b subunit 1
SLIT2: Slit guidance ligand 2
SMAD4: Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 4
SMARCA4: SWI/SNF related, matrix associated,
actin dependent regulator of chromatin,
subfamily A, member 4
TGFBR1: Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β)
receptor type 1
TLE4: TLE family member 4, transcriptional
corepressor
TP53: Tumor protein 53
TP53BP: Tumor suppressor p53-binding protein 2
U2AF1: U2 auxiliary factor 1
Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Genetic Alterations and Precision Medicine
Chi-Yuan Cheng1, Yi-Cheng, Chen1, Tzu-Cheng
Tsai1,2, Wen-Cheng Chang3
1Department of Pharmacy, Chang Gung Memorial
Hospital, Linkou
2Department of Long Term Care, Hsin Sheng Junior
College of Medical Care and Management
3Department of Oncology, Chang Gung Memorial
Hospital, Linkou
Abstract
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is the most common form of pancreatic cancer, accounting for 90% of pancreatic cancer cases. PDAC has poor prognosis with one-year survival rate of less than 20%. Currently, the treatment strategies for advanced PDAC still rely on chemotherapeutic agents. For PDAC patients with microsatellite instability, they may receive pembrolizumab, an immune checkpoint inhibitor, as the salvage therapy. In recent years, genetic alterations in PDAC are uncovered much through NGS (next generation sequencing) technique. PDAC carries 4 major mutations including KRAS, CDKN2A, TP53, and SMAD4, with KRAS mutations being the highest prevalence over 90%. Up to 24% of PDAC demonstrate defects in DNA damage repair (DDR) such as BRCA1/2 mutations, and the platinum chemotherapy (eg, cisplatin) or the PARP inhibitor (eg, olaparib) can be used as the first-line therapy for these patients. U.S. and Taiwan FDA have approved olaparib as first-line maintenance therapy of germline BRCA mutation metastatic PDAC patients whose disease has not progressed on at least 16 weeks of a first-line, platinum-based chemotherapy regimen. In addition, other clinical trials have investigated the possibility to target chromatin remodeling-related genes using DNA methyltransferase inhibitors such as decitabine and azacitidine, and histone deacetylase inhibitors such as vorinostat.
參考資料:
1. Adamska A, Domenichini A, Falasca M: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Current and evolving therapies. Int J Mol Sci 2017,18,1338.
2. Parkin A, Man J, Chou A, et al: The evolving understanding of the molecular and therapeutic landscape of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Diseases 2018;6:103.
3. 李曜珊:簡介次世代定序技術及美國的法規管理。財團法人醫藥品查驗中心當代醫藥法規月刊2017;83:1-12。(https://www.cde.org.tw/Content/ Files/Knowledge/45189bb7-1908-4797-a371-b0dee4d9fb53.pdf)
4. Ho J, Li X, Zhang L, et al: Translational genomics in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A review with re-analysis of TCGA dataset. Semin Cancer Biol 2019;55:70-7.
5. Dreyer SB, Chang DK, Bailey P, et al: Pancreatic cancer genomes: Implications for clinical management and therapeutic development. Clin Cancer Res 2017;23:1638-46.
6. Lomberk G, Dusetti N, Iovanna J, et al: Emerging epigenomic landscapes of pancreatic cancer in the era of precision medicine. Nat Commun 2019;10:3875.
7. Ng HH, Adrian Bird A: DNA methylation and chromatin modification. Curr Opin Genet Dev 1999;9:158-63.
8. Golan T, Hammel P, Reni M, et al: Maintenance olaparib for germline BRCA-mutated metastatic pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med 2019;381:317-27.
9. Qian Y, Gong Y, Fan Z, et al: Molecular alterations and targeted therapy in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J Hematol Oncol 2020;13:130.
10. Lomberk GA, Iovanna J, Urrutia: The promise of epigenomics therapeutics in pancreatic cancer. Epigenomics 2016;8:831-42.
通訊作者:鄭吉元/通訊地址:桃園市龜山區復興街五號林口長庚醫院病理大樓6樓
服務單位:林口長庚紀念醫院藥劑部/聯絡電話:(O) 03-3281200 ext 2915